Division
East Florida
Hospital
HCA Florida Westside Hospital
Specialty
Internal Medicine
Document Type
Poster
Publication Date
2023
Keywords
intracranial subdural empyema, ISE, altered mental status
Disciplines
Internal Medicine | Medicine and Health Sciences | Nervous System Diseases | Neurology
Abstract
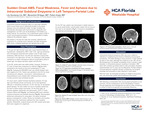
Intracranial subdural empyema (ISE) is a rare infection of brain, which occurs when pus is collectively located in the space between dura and arachnoid matter. In the past, its mortality was nearly 100%, if it was not treated appropriately within 24-48 hours. Thanks to improvement of diagnostic modalities and treatment, its mortality has dramatically decreased. Though, it can still cause a devastating consequence if it is not managed in a timely manner. The common etiology of ISE is different depending on the age group. In younger patients, it occurs frequently as a complication of infection in neighboring structures like sinusitis or otitis. On the other hand, in older patients, neurosurgical procedures are mostly related to ISE even though the incidence is low. Clinical presentation is similar regardless of etiologies, and it is more related to an anatomic region. Based on the clinical presentation and findings on imaging studies if suspicion for ISE is high, broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy must be initiated immediately. Most cases need surgical evacuation as well. We present a 76-year-old male who had a recent history of complication-free craniectomy due to a benign tumor and a month later developed AMS, fever, unilateral weakness and aphasia secondary to ISE in the left temporo-parietal lobe.
Recommended Citation
Lim, Lily Hyunjung; Nagar, Menachem M.; and Aneja, Pallavi, "Sudden Onset AMS, Focal Weakness, Fever and Aphasia due to Intracranial Subdural Empyema in Left Temporo-Parietal Lobe" (2023). East Florida Division GME Research Day 2023. 52.
https://scholarlycommons.hcahealthcare.com/eastflorida2023/52