-

It Wasn’t a Duck: A Case of the Misdiagnosis of Ketoacidosis
Shiva Mohan, Brandon Vu, and Danielle Ford
Introduction Most clinicians have heard the old adage: if it looks like a duck, walks like a duck, and quacks like a duck, it’s a duck. However, this is not always true. Ketoacidosis is a complicated physiological state resulting from fatty acid and amino acid degradation often associated with type 1 diabetics. It can also arise with excess alcoholism, pregnancy, starvation, and exercise. Diabetic, alcoholic, and starvation ketoacidosis may present similarly. Clinicians can often mistake alcoholic and starvation ketoacidosis for diabetic ketoacidosis due to its common presentation. We present a case of a young non-pregnant woman with a history of alcoholism, treated on several admissions for presumed diabetic ketoacidosis, whose ketoacidosis improved clinically with treatment targeted at starvation ketoacidosis and without the administration of insulin. Case Presentation A 31-year-old woman with a past medical history of alcoholism presented with a five-day history of diffuse achy abdominal pain and intermittent nausea and vomiting. She endorsed increased urinary urgency, fatigue, decreased appetite, and 20 pounds of unintentional weight loss. In the preceding five months, she was admitted three times with similar symptoms and was diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis. She was treated with and discharged on insulin each visit. She was initially compliant with her home insulin regimen but stopped taking it due to recurrent hypoglycemia. Her workup was significant for a blood glucose of 240 mg/dL, an anion gap of 15 mmol/L, and an elevated serum beta-hydroxybutyrate of 26.64 mg/dL. Her hemoglobin A1C was normal at 5.5%. She was symptomatically managed with antiemetics and intravenous (IV) hydration. Crucially, her blood ketone and glucose levels normalized without insulin but with the initiation of a dextrose and water infusion and IV thiamine. She was discharged on oral thiamine, and her home insulin was discontinued. Her thiamine level was confirmed low at 51.9 nmol/L post discharge. Discussion The presence of ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia may cause clinicians to suspect diabetic ketoacidosis; however, this may be a misdiagnosis. Our patient’s initial hyperglycemia was likely multifactorial from rebound hyperglycemia after inappropriate insulin administration, stress-induced, chronic alcohol use, and starvation ketoacidosis. Our patient was initially diagnosed with pre-diabetes. She was subsequently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2, with non-compliance to insulin. The diagnosis was carried forward for several encounters despite a normal hemoglobin A1C and hypoglycemia with insulin administration. This case highlights the importance of looking holistically at a patient’s case without prejudice, persuasion, or repetition of previous diagnoses without consideration of alternatives.
-

Lesion Size Inclusion on Dermatopathology Requisition Forms: a Quality Improvement Project
Christopher M. Wong, Henry Lim, Christian Scheufele, Daniel A. Nguyen, Ashleigh E. Hermann, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Introduction: Dermatopathology requisition forms (RFs) are a critical communication tool between dermatologists and dermatopathologists. Including detailed information on RFs improves the diagnostic accuracy of the consulting dermatopathologist. However, the diameter of the biopsied lesion is often omitted on RFs. This study aimed to increase the rate of reporting lesion diameters on RFs from an academic outpatient dermatology clinic to greater than 65% through education, reinforcement, and evaluation. Methods: This quality improvement project retrospectively and prospectively analyzed the inclusion rate of lesion diameters on dermatopathology RFs from a single institution. In Phase 1, data was collected from all skin biopsies performed between July 1, 2021 and February 4, 2022, and the presence or absence of lesion diameters on RFs was recorded. A single intervention was conducted on February 4, 2022 to educate the authors on societal guidelines for reporting lesion diameters on RFs. Phase 2 evaluated short-term efficacy through data collection and analysis of RFs for biopsies obtained from February 5, 2022 to June 14, 2022. Long-term efficacy will be assessed through data collection and analysis of RFs for biopsies obtained from January 1, 2023 to June 30, 2023. Results: During Phase 1, 839 skin biopsies were performed, with 594 biopsies meeting the criteria for analysis. 49 samples included lesion diameters, resulting in a final reporting rate of 8.25%. In Phase 2, after the intervention, there was a statistically significant reporting rate increase to 49.71% (85/171) in the intervention group (chi-squared test, p < 0.001). The intervention group had a statistically significant increase in reporting rate compared to the control group not receiving the intervention (1.73%, 5/289, chi-squared test, p < 0.001). Long-term efficacy results from Phase 3 are yet to be reported. Conclusion: The intervention in this study successfully increased the rate of reporting lesion diameters on RFs from an academic outpatient dermatology clinic, demonstrating the importance of education and reinforcement in improving quality. Further studies will determine the long-term efficacy of the intervention.
-
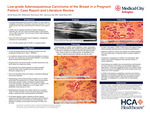
Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast in a Pregnant Patient: Case Report and Literature Review
David Bassa, Makenzie Morrissey, Adewuni Ojo, and Adeel Raza
Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast: Case Report and Literature Review Authors: David Bassa DO, MaKenzie Morrissey MD, Adewuni Ojo MD, Adeel Raza MD Abstract: Introduction: Low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma (LGASC) is a rare variant of metaplastic carcinomas of the breast. It is characterized by its clinical indolence and low-grade cytomorphology. Presentation is typically asymptomatic with indeterminate imaging characteristics with diagnosis dependent solely on histopathology findings. We herein describe a case of LGASC presenting in a young premenopausal female, an extremely rare occurrence. Case presentation: A 23-year-old woman presented to the breast clinic with a left breast ultrasound demonstrating a heterogeneous ill-defined hypoechoic area in the left upper inner quadrant. She stopped breastfeeds three years postpartum and noticed a palpable left breast mass a week later. She was otherwise asymptomatic. A left breast biopsy revealed stromal fibrosis and an ultrasound-guided excisional biopsy revealed sclerosing adenosis and fibrocystic changes. Due to the discordant clinical findings, both biopsies were sent to Weill Cornell Medicine for histopathological review. The review revealed low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma arising within the background of a complex radial sclerosing lesion. The tumor was ER low positive, PR positive, and HER2 negative. Conclusion: LGASC of the breasts remains a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Despite being a variant of metaplastic breast carcinomas, which present as triple negative tumors with poor prognosis, this indolent lesion has a more favorable prognosis when recognized early. Given the rarity of this cancer, there are no current guidelines for best practice management of adjuvant chemoradiation. Keywords: Low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, metaplastic breast cancer, sclerosing lesions of the breast, indolent breast cancer
-

Monitoring Concordance in the Management of Transfusing Blood Components in Cirrhotic Patients for Paracentesis with Evidence-Based Guidelines
Joseph Kim and Gregory Moses
Initiative to decrease unnecessary hemostatic agent transfusion in cirrhotic patients undergoing paracentesis: a resident-led approach quality improvement project to prevent transfusion overuse. Currently, there is no official guideline placed in the hospital for the administration of a hemostatic agent such as fresh frozen plasma in the setting of an elevated international normalized ratio, which paradoxically is an anticipated finding in cirrhotic patients. This process leads to unnecessarily prolonging the duration of the hospital course due to delays in performing the interventional procedures and interruptions in scheduling. The goal of this project is to educate and provide physicians with the most recent guidelines for managing bleeding risks with periprocedural procedures.
-

Outpatient Breast Cancer Screening Documentation
Christoffer A. Amdahl and Jeremy Smith
Introduction: Over 264,000 cases of breast cancer are diagnosed annually within the United States, with 99% of them being in women. Regarding prevention of this terrible disease, early detection of such cancers through screening mammography has up to a 20% reduction in breast cancer mortality. Therefore, the USPSTF recommends screening of women who are 50-74 years of age via mammography at average risk of breast cancer every two years. The goal of this study was to measure, track, and increase compliance with these screening recommendations within the Medical City resident clinics.
Method: Family medicine residents working were presented with a standardized electronic medical record template to improve the rate of recorded breast cancer screenings within appropriately aged women. The template would be used for patients who are referred for the imaging study, and completed once the patient presented the results of the completed study. Residents were additionally tracked on how many patients they appropriately referred for screening. Education was given to all residents and nurses responsible for the referral process and on the importance of the correct implementation and recording of a successful mammogram referral. The developed protocol was used within the Family Medicine outpatient clinic sites at Grand Prairie, North Hills, and Denton to increase screening compliance.
Results: All three clinic sites measured in the study showed an overall compliance rate of 17.35%. Data was also grouped by resident year and individual. However, this data may not represent the true compliance rate, as reports were frequently not attached to the initial screening template order by nursing staff secondary to high clinic staff turnover rates.
Conclusion: Efforts to improve compliance with current USPSTF guidelines on breast cancer screening were not reflective of adherence to the standardized template, and will require additional study design improvement. Additional cycles of the study will feature nursing specific education didactic sessions regarding proper, and data from both pre- and post- education sessions will be compared to measure true resident screening compliance rates.
-

PHQ -9 Utilization in the Primary Care Setting
Michael Armstrong, Ramisa Rahman, Ceferino Cruz IV, and Afsha Rais Kaisani
INTRODUCTION: The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) is a tool used to help diagnose depression and assess a patient’s response to treatment. Quality metric (QM) 371 is a measure of PHQ-9 utilization in patients with depression, and Medical City Family Medicine tracks QM 371 in order to improve the quality of care provided to our patients. This project sought to assess utilization of the PHQ-9 in our clinical practice. At the time of this QI project’s inception, QM 371 was reporting at 0%.
METHODS: Our intervention was to give an educational presentation regarding depression, the PHQ-9, as well as how to properly document the PHQ-9 in eClinicalWorks (eCW) for data tracking. QM 371 is calculated as follow: the denominator includes patients 12 years and older with a diagnosis of Major Depression or Dysthymia within the eligible 4-month period, and the numerator includes all patients age 12 and older that have completed the PHQ-9 at least once within the 4-month period. Our educational presentation was given on Sept 1st at the start of the reporting period for QM 371 and included screen shots depicting the workflow for inputting the PHQ-9 into the eCW smart form.
RESULTS: A data query 2 months in showed that QM 371 continued to measure 0%, however the authors of this study knew that a value of 0% should not be possible. We at least, were properly documenting PHQ-9 utilization. The query was escalated multiple times until it was discovered that Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) discontinued QM 371. The Division Director of Quality Initiatives provided us with the data that QM 371 would have been tracking if it were still in use. The results indicate that all three clinical sites, at the time of the data query, were close-to or at the goal of 22.09%. Data received mid-November showed the Arlington site at 17.82%, the North Hills site at 26.32% and the Denton site at 22.41% year-to-date (YTD).
CONCLUSION: It was discovered that QM 371 was discontinued by CMS, unbeknownst to anyone in our organization. Our QI project identified a major gap between our clinical practices, in this case use of the PHQ-9, and the clinical informatics that were being reported. Awareness of this gap creates opportunity to determine a new way to measure and improve the quality of care we provide to patients with depression.
-

Platelets in Preeclamptic Pregnancies Fail to Exhibit the Decrease in Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption Rate Seen in Normal Pregnancies
Joseph Kim, Andrew Malinow, and Rosemary Schuh
Cellular oxygen consumption and lactate production rates have been measured in both placental and myometrial cells to study obstetrics-related disease states such as preeclampsia. Platelet metabolic alterations indicate systemic bioenergetic changes that can be useful as disease biomarkers. We tested the hypothesis that platelet mitochondria display functional alterations in preeclampsia. Platelets were harvested from women in the third trimester of either a healthy, non-preeclamptic or preeclamptic pregnancy, and from healthy, non-pregnant women. Using Seahorse respirometry, we analyzed platelets for oxygen consumption (OCR) and extracellular acidification (ECAR) rates, indicators of mitochondrial electron transport and glucose metabolism, respectively. There was a 37% decrease in the maximal respiratory capacity measured in platelets from healthy, non-preeclamptic compared with preeclamptic pregnancy (P
-

Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: Assessing Medical City Weatherford Resident Physicians’ Knowledge in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Hiral Thakkar and Aaron Kolar
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) is a relatively understudied sequelae of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). PTS typically presents with similar signs and symptoms as chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and treatment modalities also mirror each other with the use of compression therapy, emollients, and topical steroids. The contrast is PTS is a direct result of a DVT, and DVTs can be prevented. Thus, it is essential that physicians are able to differentiate and effectively treat both PTS and CVI. Since PTS is widely understudied, the goal of our project is educate residents and other medical professionals on the full scope of PTS including pathophysiology, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis through a single-session one-hour oral presentation. We will measure resident knowledge through a short survey/assessment administered before and after the presentation. We expect that the oral presentation will lead to a score increase of 20% from pre-survey to post-survey. These results would suggest that our target audience will be more conscience of preventing DVT; as well as, treating patient’s appropriately when they present with PTS. Therefore, this improvement on the survey will lead to better patient care, improvement of quality life and reduction in healthcare cost.
-

Presentations of Tumor Recurrence of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer After Treatment with Low-Energy Superficial Radiation Therapy
Marshall Hall, Henry Lim, Christian Scheufele, Christopher M. Wong, Daniel A. Nguyen, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Background: Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of non-melanoma skin cancers.1 Superficial radiation therapy (SRT) is a treatment modality that utilizes low-energy x-rays to disrupt cell mitosis.2 While this technique has been used for over a century, it has recently gained favor in clinical practice.3,4 This method of treatment offers favorable outcomes and advantages for select patients. Although the incidence of cancer recurrence after superficial radiation therapy is low, relatively little is known regarding predictive patterns. The frequency and timing of cancer recurrence is not well defined using SRT delivered technology with an image-guided approach utilizing high-frequency ultrasound capabilities.3,5 Methods: A retrospective chart review study was performed on patients treated with image-guided SRT at an academic dermatology clinic between December 2018 to December 2021. Follow-up was through December 2022. Demographic information and medical history related to the population were analyzed as part of the data set. Treatment failure and cancer recurrence were monitored to compare possible differences in treatment response. The primary endpoint was any histologically confirmed non-melanoma skin cancer identified within the treatment field at any follow-up visit. Results: There were 341 non-melanoma skin cancers treated with SRT in 165 individuals during the reviewed dates. Out of 341 individual cases of malignancy, four were suspected of recurrence during follow-up visits. Subsequently, all four cases were biopsied and confirmed histologically as cancer recurrence. All of the relapses originally had squamous cell carcinoma. None of the patients with basal cell carcinoma relapsed. The time frame for recurrence varied between 3 to 18 months after the final treatment visit. All four cases of recurrences were found in adult males, and the cancers were limited to the head and neck area. Conclusion: Cancer recurrence outcomes of persons treated with high-frequency ultrasound-guided SRT were comparable to those reported for surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer. Further prospective studies with longer follow-up periods would be valuable to in assessing the risk of recurrences after SRT, and to refine treatment protocols to minimize treatment failures and tumor recurrence. This would improve patients’ ability to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options for non-melanoma skin cancer.
-
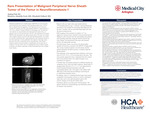
Rare Presentation of Primary Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of the Femur in Neurofibromatosis-1
Akshaj Pole, Danielle Ford, and Elizabeth Pollard
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) are rare sarcomas, most commonly seen in patients with Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), that are characterized as aggressive with high rate of local recurrence. Among NF1 patients, the risk of developing MNPSTs is approximately 8-13% over a lifetime. Primary MPNST is exceedingly rare, of which the vast majority are concentrated in the head and neck region. Here, we present a case of a 40-year-old male with NF1 who presented with a giant MPNST that originated in the right proximal femur. The mass was treated with complete surgical resection with right hip disarticulation. In a matter of 4 months, the patient had a rapid progression with metastatic disease to the brain and lungs. We will use this case as an opportunity to explore the current guidelines for post-surgical malignant sarcomas especially in those with neurofibromatosis and the need for more aggressive and active adjuvant treatments.
-

Retrospective Review of Adverse Events Following Treatment of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer with Low-Energy Superficial Radiation Therapy
Marshall Hall, Henry Lim, Christian Scheufele, Christopher Wong, Daniel A. Nguyen, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Background: Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of non-melanoma skin cancer.1 Superficial radiation therapy (SRT) is a treatment modality that utilizes low-energy x-rays to disrupt cell mitosis directly and indirectly.2 This method of treatment offers advantages for select patients. While this technique has been utilized for over a century, it has recently begun to gain favor in clinical practice.1,3 Although SRT has shown favorable outcomes with a low risk of complications, it still poses a risk for adverse events.1,3,4 The frequency and severity of adverse events are not well-defined with SRT delivered technology with an image-guided approach utilizing high-frequency ultrasound capabilities.3,5
Methods: A retrospective chart review study was performed on patients treated with image-guided SRT at an academic dermatology clinic between December 2018 to December 2021. Demographic information and medical history related to the population were analyzed as part of the data set. All patients were questioned about risk factors for radiation complications, including a history of cutaneous lupus, prior to SRT. Complications were defined as adverse events within the treatment site persisting beyond the treatment period. Adverse events including erythema, desquamation, radiation dermatitis, and radiation necrosis were collected during the treatment period and subsequent follow-up visits. The primary endpoint was any dermatologic diagnosis or condition requiring treatment beyond the 2-week follow-up visit.
Results: Three of 165 patients treated with SRT during the reviewed dates experienced adverse events beyond erythema and desquamation during the treatment period. Two patients experienced ulceration of the lower extremities. Both patients with ulcerations had venous stasis with chronic edema. One patient developed radiation-induced cutaneous lupus erythematosus. The patient who developed cutaneous lupus after therapy had no prior history systemic or cutaneous lupus.
Conclusion: Treatment complications were rare, and all were expected complications of radiation therapy. They occurred despite precautions intended to minimize these complications. High-frequency ultrasound image-guided SRT is a well-tolerated treatment for non-melanoma skin cancer. Conducting further controlled studies on adverse events, risk factors, treatments, and prevention strategies for non-melanoma skin cancer would enhance patients’ ability to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options.
References: 1. McGregor S, Minni J, Herold D. Superficial Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. Dec 2015;8(12):12-4. 2. Gianfaldoni S, Gianfaldoni R, Wollina U, Lotti J, Tchernev G, Lotti T. An Overview on Radiotherapy: From Its History to Its Current Applications in Dermatology. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. Jul 25 2017;5(4):521-525. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.122 3. Han H, Gade A, Ceci FM, Lawson A, Auerbach S, Nestor MS. Superficial radiation therapy for nonmelanoma skin cancer: A review. Dermatological Reviews. 2023;3(6):409-417. doi:10.1002/der2.174 4. Hernandez-Machin B, Borrego L, Gil-Garcia M, Hernandez BH. Office-based radiation therapy for cutaneous carcinoma: evaluation of 710 treatments. Int J Dermatol. May 2007;46(5):453-9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.03108.x 5. Yu L, Oh C, Shea CR. The Treatment of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer with Image-Guided Superficial Radiation Therapy: An Analysis of 2917 Invasive and In Situ Keratinocytic Carcinoma Lesions. Oncol Ther. Jun 2021;9(1):153-166. doi:10.1007/s40487-021-00138-4
-
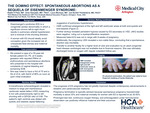
The Domino Effect: Spontaneous Abortions as a Sequela of Eisenmenger Syndrome
Riddhiben Patel, Anas Hamadeh, and Senthil Thambidorai
Background: Eisenmenger's syndrome (ES) is a congenital cardiac abnormality in which a significant chronic left-to-right shunt results in pulmonary arterial hypertension and a reversal of the shunting direction. A woman with ES should ideally avoid conception given the increased risk of unexpected fetal demise and maternal mortality. Case: We present a case of a 35-year-old female patient G3, P0, at 9 weeks gestation with reported PMHx of erythrocytosis and spontaneous abortions who presented to the hospital with complaints of vaginal bleeding and worsening SOB. She was noted to have a Hct of 70 and a Hb of 23.8, with SaO2 of 86% on room air upon initial evaluation. A transthoracic echocardiogram revealed a medium to large perimembranous ventricular septal defect (VSD) measuring 6 mm with predominantly right to left shunting with a QP/QS ratio of 0.66. The patient's right ventricle was dilated with systolic and diastolic septal flattening suggestive of pulmonary hypertension. CMR confirmed enlargement of the right and left ventricular areas at both end-systole and end-diastole. Further workup revealed persistent hypoxia caused by ES secondary to VSD. JAK2 studies were negative, ruling out a myeloproliferative neoplasm. Measured beta-hCG was not in range with 9-weeks of pregnancy. Additionally, the pregnancy USS revealed a non-viable fetus, concluding that a spontaneous abortion was inevitable. Transfer to another facility for higher level of care and evaluation by adult congenital heart disease cardiologist was not available due to financial reasons. She was ultimately discharged home on oxygen with regular outpatient follow ups. Conclusion: The prognosis of ES pregnancy has not greatly improved despite contemporary advancements in obstetric and cardiovascular medicine. Pregnancy termination is typically advised because spontaneous pregnancy loss/perinatal morbidity are about 30% and maternal mortality for women with ES is reported to be 30-50%. Prolonged bed rest, continuous oxygen therapy, and anticoagulation under hemodynamic observation can positively influence maternal and fetal outcomes.
-

West Nile Virus Encephalitis with Status Epilepticus Treated with High-Dose Steroids: A Case Study
Sherwin Thomas and Sawroop Sandhu
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus endemic in the United States. WNV infection can present with a variety of non-neurologic and neurologic symptoms. Patients who present with WNV neuroinvasive disease have significant morbidity and mortality, with about 10% of cases resulting in death. There is currently no evidence-based treatment for WNV infection. Management is typically with supportive care. Some limited data shows corticosteroids as a possible treatment for neuroinvasive disease. This case report discusses a 55-year-old female patient who presented with altered mental status. She was found to be septic overnight and was found to be in status epilepticus on EEG. The patient was intubated and sedated, started on multiple antiepileptic medications. Sepsis workup was initiated, and empiric antibiotics were started. A lumbar puncture was performed, showing findings consistent with a viral encephalitis. Continuous EEG showed frequent seizures and other epileptiform discharges. Due to no significant improvement, the patient was started on high dose intravenous corticosteroids. The infectious workup eventually revealed that the patient had West Nile virus infection. With the antiepileptic medications and high dose steroids, the patient had a rapid recovery. She was soon able to be extubated and discharged to a rehab facility. There are some conflicting data, with case reports and small retrospective studies, about the efficacy of corticosteroids in the management of WNV neuroinvasive disease. A possible mechanism is corticosteroids having anti-inflammatory properties that can improve the perivascular inflammation associated with WNV neuroinvasive disease. High dose corticosteroids were found to be very effective for the management of WNV neuroinvasive disease in this case.
Featuring scholarly activity by HCA Healthcare Graduate Medical Education residents from the North Texas Division.
A conference program is available here.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

