
North Texas Research Forum 2025
On April 18, 2025, Medical City Arlington hosted the North Texas Division Research Forum with 200+ attendees (in-person & virtual), over 350 authors, 12 oral presentations, 46 in-person poster presentations, and 50 virtual poster presentations celebrating scholarly activity from the North Texas Regional Consortium of Medical City Healthcare, University of North Texas (UNT), and Texas Christian University (TCU). The forum was honored to have Dr. Kimberly Washington, MD, FACS - Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, Assistant Dean of Clinical Faculty Success & Engagement, TCU and Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, Texas Health Physician Group as the keynote speaker focusing on “Patient Experience: Oncologic Surgery”.
Research Category Winners
- 1st Place: McKenna Box, Neil Werthmann, Troy Puga, Andrew Jen, Yingxian Liu, and John Riehl - A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study of GLP-1 Agonist Effects on Outcomes after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- 2nd Place: Luke Taylor, Otoniel Espinoza, Omar O. Hernandez, Shannon Biggers, Shirin Miller, Srinivas Yallapragada, Amer Alaiti, Andrew Fredericks, Song Li, and Claudius Mahr - Use of VA ECMO in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Presenting with Obstructive Cardiogenic Shock undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy
- 3rd Place: Troy Puga, Tanner Haechten, Cole Cush, Hans Drawbert, and John Riehl - NFL Kick-off Rule Change: A Comparative Analysis of Injury Incidence
Quality Improvement Category Winners
- 1st Place: Matthew Gutzmer, Michele L. McCarroll, Christian Scheufele, Zara Soomro, Ali Nazim, Enith Espinosa-Palmett, Marshall Hall, Taylor Pickering, Garrett Furth, Jasmine Silva, Shterna Frand, Shana Lambert-Johnson, Jeff Dickerson, Henry Lim, Ali Al-Nahi, Kelly Mofor, Lakshmi Morla, Nischal Pokhrel, Brina Gonzalez, Rui Zhang, Sana N Khan, Devika Adusumilli, and Sherri Morgan - Improving Nursing Professional Practice-Based Application Using the Latest Evidence-Based Approaches in Dermatology and Diabetes
- 2nd Place: Makenzie Morrissey, Kristen Payne, Randall Rittmann, Chris Robert, Joseph Lim, and Danielle Pigneri - Improving Communication and Follow Up for Incidental Findings from PanScan Imaging
- 3rd Place: Sumanth Reddy, Artur Amirkhanyan, Jeremiah Avarana, Praneetha Arge, and Alicia Lay - Effective Communication in the Pronunciation of Brain Death
Case Report Category Winners
- 1st Place: Dakota Dalton, Elizabeth White, and Christopher Medina - Efficacy of Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment in Post-Stroke Recovery Patients
- 2nd Place: Rafael Do Valle, Reem Ayoub, Henry Lim, Marshall Hall, and Stephen Weis - Clinical Evaluation and Management of Terra Firma-Forme Dermatosis: Insights from Two Diverse Cases
- 3rd Place: Shana-Kay Lambert-Johnson, Rui Zhang, Brian Yu, and Tasaduq Mir - Humoral Influences on the Heart: A Case of Overt Hypothyroidism and Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Acute Heart Failure
Posters and presentations are also available at the North Texas Division GME Research Forum Gallery here.
-

Heterotopic Ossification (HO) Prophylaxis in Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA): A Systematic Review of Level I and Level II Evidence Since 2000
Troy Puga, McKenna Box, Vincent Dieu, Charles Marchese, and John T. Riehl
Introduction: Heterotopic ossification (HO) is a somewhat common occurrence after total hip arthroplasty (THA), particularly with certain approaches. This complication can be detrimental to the success of the surgical outcome. Indomethacin and radiotherapy remain common treatment modalities; however, no true gold-standard treatment is universally agreed upon. This study aims to evaluate Level I and Level II evidence for treatment practices of HO prophylaxis since 2000. Methods: To evaluate HO prophylaxis in total hip arthroplasty, a search was conducted across MEDLINE/Pubmed, Cochrane, and Embase databases using keywords and Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms. Titles and abstracts were screened for eligibility for inclusion criteria. Full texts were screened and included if they met eligibility criteria. Results: HO chemical prophylaxis was more effective than no HO prophylaxis, except for aspirin. Multiple NSAIDs showed equivalence and better side effect profiles than indomethacin. No one superior NSAID was found, and numerous modalities showed efficacy. The most effective dosages of radiation therapy and combination therapy remain unclear. Additionally, both etidronate and salmon calcitonin showed benefit in preventing HO in one study each. Conclusion: Radiation, NSAIDs, and combination therapy all showed efficacy as HO prophylaxis modalities. HO prophylaxis treatment and modalities should be guided upon patient and surgical factors such as surgical approach, side effects and tolerability of modalities, comorbidities, and available facility resources to optimize the prevention of HO.
-
Humoral Influences on the Heart: A Case of Overt Hypothyroidism and Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Acute Heart Failure
Shana-Kay Lambert-Johnson, Rui Zhang, Brian Yu, and Tasaduq Mir
BACKGROUND/INTRODUCTION: Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) affects approximately 7 in 100,000 adults annually, with a mortality rate of 50%. It is typically idiopathic, progressive, and irreversible. However, in the context of hypothyroidism, DCM can be reversible. Hypothyroid-induced DCM with coexisting systolic dysfunction is a rare occurrence. This case report presents an exceptional instance of this phenomenon, highlighting the critical role of thyroid hormone replacement in improving patient outcomes. CASE PRESENTATION: A 48-year-old female with a medical history of hypothyroidism (post-thyroidectomy) was transferred for higher-level care due to new-onset heart failure. Over the past five months, she experienced worsening dyspnea on exertion, fatigue, and bilateral leg swelling with a concomitant lapse in thyroid replacement therapy. Upon admission, the B-type natriuretic Protein (BNP) level was 990, troponin was 1221, and the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) level was 162, indicating heart failure and possible myocardial injury with severe hypothyroidism. Cardiac catheterization revealed patent coronary arteries. Transthoracic echocardiography demonstrated severe left ventricular dilation and a reduced ejection fraction of 10-15%, consistent with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy. The heart failure team was consulted, and treatment was promptly initiated with intravenous levothyroxine and oral liothyronine for thyroid hormone replacement and digoxin to support myocardial contractility. Due to hypotension, guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) was limited. Despite this, the patient showed remarkable improvement in her symptoms, including reduced edema, improved fatigue, and better exercise tolerance. LEARNING POINTS: This case underscores the potential for improved outcomes in hypothyroid-induced DCM and systolic dysfunction with timely thyroid hormone supplementation. As the degree of reversibility may be diminished if treatment is delayed, it is crucial to assess thyroid function and promptly initiate thyroid hormone replacement when necessary. The patient had not received thyroid supplementation for five months before admission. Remarkably, she experienced significant symptom improvement despite limited guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), following thyroid hormone replacement. This outcome highlights the potential for reversing DCM and acute heart failure with appropriate treatment, emphasizing the critical need for early detection and management of thyroid dysfunction to optimize cardiac health.
-

Hydralazine Induced ANCA Vasculitis
Justin Huang, Yasasvi Sabbineni, Sumanth Reddy, and Hani Khair
Hydralazine is a vasodilator commonly used for hypertension. Hydrazine is commonly used in patients who can not tolerate ACEs and ARBs, resistant hypertension, and during pregnancy. Hydralazine has also been implicated in ANCA-associated vasculitis and drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Vasculitis is the presence of inflammatory leukocytes in vessel walls, inflammation can cause loss of vessel integrity which can lead to bleeding and downstream tissue ischemia and necrosis. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (AΝCΑ)-associated vаsсulitiѕ (ΑΑV) is a necrotizing vаsсսlitis that does not substantially involve the deposition of immune complexes. AΑV predominantly affects small vessels and is associated with ANСΑ specific for myeloperoxidase (MPO-ΑNCΑ) or proteinase 3 (PR3-ΑNСA). Drugs that are commonly associated are propylthiouracil, methimazole thiamazole, carbimazole, hydralazine, and minocycline. Hydralazine is the most common cause. Early detection is vital as cessation of offending medication leads to the resolution of disease progression.
-

Hypothyroidism Associated Hyponatremia, A Complicated Presentation
Gary Lee, Spencer Steinberg, Samiuallh Shahid, Evangelista Ezenduka, and Edgardo Flores
Introduction: Hypothyroidism is a well known text-book cause of euvolumic hyponatremia that is a rare occurrence in clinical practice in the absence of other potential etiologies of hyponatremia. We review a case of a 48 year old female presenting with profound generalized weakness found to have severe hyponatremia, later found to have severe hypothyroidism during admission. We review the potential mechanisms whereby hypothyroidism results in hyponatremia and whether or not hypothyroidism-induced hyponatremia truly exists and the current evidence supporting these views Case Presentation: 48 year old female with history of hypothyroidism, breast cancer post right lumpectomy and radiation presented for a few day history of generalized malaise and weakness found to be hypothermic and bradycardic with a notable sodium level of 109. Patient eu-volumic on physical exam. Further history reviewed that she only took “supplements” for her hypothyroidism and not any pharmacological thyroid replacement. Patient brought to ICU where hyponatremia was corrected. TSH and T4 were obtained and had a value of 39.160 uIU/mL and .16 ng/dL, respectively. Thyroid hormone replacement initiated as well as IV steroids. Other potential causes of hyponatremia including depleted intra-vascular volume and medications were ruled out. Patient’s clinical course was complicated with rhabdomyolysis resulting in compartment syndrome necessitating fasciotomy of the lower extremities. Patient did well in the end with sodium normalizing and previous presenting symptoms resolved. Patient was sent home on levothyroxine with close PCP follow up Conclusion and Learning points: Hypothyroidism-induced hyponatremia remains a known, but rare, entity in everyday clinical practice. Proposed mechanisms include, but are not limited to, the activation of anti-diuretic hormone in the face of decreased glomerular-filtration rate, baroreceptor mediated release of vasopressin, and reduction of Na-K-ATPase activity leading to reduced tubular sodium reabsorption. Evidence regarding these mechanisms is conflicting. It remains that there is no absolute causal relationship between hypothyroidism and hyponatremia. Therefore, it is imperative to evaluate for other causes of hyponatremia in hypothyroid patients in the clinical setting
-

Implementing Intermittent Fasting Education for Improved A1C Control in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Dakota Dalton, Elizabeth White, Malinda Hansen, and Tasaduq Mir
Background: Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the UNTHSC Family Medicine clinic varies among residents, with some advocating robust lifestyle counseling and others relying more on medical management. This leads to inconsistencies in patient education and treatment strategies. Lifestyle interventions such as dietary modifications, are unfortunately too often underutilized in the clinic and in primary care in general, despite strong evidence supporting their efficacy in control of both A1C measurements and random fasting blood sugar, and improved prognosis of diabetes. To address this, we have designed and introduced an intermittent fasting (IF) handout as a supplemental standardized educational handout for diabetic patients not on insulin (as fasting while on insulin can be dangerous). This Quality Improvement project's goal is to assess the impact of this strategy IF education on A1C control and evaluate the handout's effect on the utilization of lifestyle modifications in the management plan of the above patients (including those patients managed by residents, attendings, and APPs willing to participate in this endeavor). Methods: A planned retrospective review of 30 randomly selected patient charts with a diagnosis of T2DM (excluding those currently managed with insulin) will be conducted to assess baseline recommendations and treatment strategies - to answer the question: "how often are we recommending lifestyle interventions to patients?" A1C control will also be reviewed. Following this review, participating physicians and APPs will be given the above described IF handout to distribute to eligible patients. The intervention's efficacy will be evaluated by tracking changes in A1C over a designated follow-up period, proposed 6 months. Data will be collected on provider adherence to distributing the handout and any documentation of patient's willingness to adhere to IF as a dietary strategy. Results: Key metrics include the percentage of eligible patients meeting the above criteria who received the IF handout, their adherence to the intervention, and subsequent changes in A1C levels. Further analysis may explore reported barriers to IF recommendations and implementation. Conclusions: With this Quality Improvement project, we hope to standardize dietary education with regard to IF for T2DM patients, and assess the feasibility of this strategy as a lifestyle intervention with out patient population. The results will inform future efforts and projects to improve patient education and compliance, improve glycemic control, and refine our clinic's approach to managing diabetes with non-pharmacologic approaches.
-

Improvement in Prenatal Education and Involvement in Patient Care
Miranda Ibrahim, Christelle Reeves, and Timothy Kremer
BACKGROUND: While the attempt is to educate the patient (and their family members) and empower them in their medical decision making, integration of birth plans and discussion of such plans is not routinely implemented by most obstetrical providers. There is currently no standardized approach to the education and birth plan development/or the obstetrical patients. The goal of this project, therefore, is to develop a standardized approach to discussion of birth plans and, albeit indirectly, allow for an opportunity for education for obstetrical patients. METHODS: On a daily basis, through birth plan discussions with patients during routine obstetrical visits, and via questionnaire implementation during postpartum visits, we will be collecting information. The patients we care for in our GME clinic will be the patient population we will utilize. Documentation on eCW and collection of patient feedback/opinions regarding birth plan discussions through a questionnaire is how we will keep track of the data collected. RESULTS: While the results of this study are still pending and more PDSA cycles will be completed and data collected, we expect nearly full compliance with regards to implementation of this QI project at the GME clinic setting. We anticipate an increase in patient education and patient satisfaction when it comes to the care they receive during their pregnancy at GME clinic at Medical City Arlington. CONCLUSION: Implementation of this project would allow us to improve patient satisfaction, open discussion/dialogue between provider and patient during routine obstetrical visits, and the preparedness of L&D staff when it comes to a laboring patient’s preferences according to their birth plan. Retrospective data from this study will be used to propose a standardized birth plan form to be used at the GME clinic and perhaps to be used/distributed to other facilities for use as well, in hopes of utilizing a standardized approach to discussion of birth plans and allow for an opportunity for education for obstetrical patients.
-

Improving Annual Wellness Visit Documentation in Clinic
Chak Lam Yeung, Gurunath Subramanyam, Krishna Ramesh, Mohammad Nadim, Jasmyne Bowser, and John Sturgeon
Introduction: Medicare beneficiaries who received an annual wellness visit (AWV) were noted to have reduced Medicare spending. Review of Medical City North Hills Internal Medicine Clinic data showed that 44% of eligible patients received an AWV. Improper documentation and coding were the primary reasons eligible AWVs were not accounted for even though they were performed. Majority of incomplete documentation was missing information regarding patient’s functional ability, level of safety, home safety, and activities of daily living. The information is normally obtained from a questionnaire completed by the patient prior to the visit. Questionnaire was noted by residents to be unorganized and contain extraneous information. The goal of the QI project is to improve resident documentation via revision of patient questionnaire. Methods: The original questionnaire was first examined and compared to the electronic medical record template used for AWV. Extraneous questions were removed and remaining questions were reorganized into respective categories of functional ability, level of safety, home safety, and activities of daily living. Draft questionnaire was reviewed by front office staff and sent to HCA Healthcare administration for final approval. Revised questionnaire was implemented February 2024. Proper documentation of AWV since implementation of questionnaire is currently being evaluated on a monthly basis. Individual AWVs will be reviewed to ensure documentation of the mentioned categories is included in the visit. Compliance rate will be calculated based on number of properly documented AWVs out of total AWVs that month. Results: Data regarding compliance with new questionnaire is currently being collected. Discussion: Low AWV rate at the Medical City North Hills clinic is due to multiple factors. Incomplete documentation by residents, improper use of billing codes, and limited familiarity with clinic EMR are some examples. Improvement in documentation rate should be ideally achieved through first fixing and optimizing the questionnaire so that the information can be input easier.
-

Improving Colon & Rectal Cancer Screening at Medical City North Hills Clinic
Basil Nduma, Sharvani Raguthu, Gurunath Subrahmanyam, and John Sturgeon
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Despite its severity, fewer than half of eligible Americans undergo annual screening. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends CRC screening from age 45 to 75, with personalized assessments for those aged 76 to 85. The current CRC screening rate at the Medical City North Hills Internal Medicine Residents’ Clinic is 9.3%, significantly below the target rate of over 66%. Objective: This project aimed to increase the CRC screening rate from 9.3% to over 66% at the Medical City North Hills Internal Medicine Residents Clinic, in line with USPSTF recommendations. Method: Barriers to screening were identified, including acute medical issues, high screening costs, and inefficient workflows, improper documentation of screened patients, and inadequate education of resident physicians and other clinic staff on CRC screening. Cost-free solutions were implemented, such as re-education on CRC screening guidelines, proper documentation in the electronic medical record (eCW), and workflow modifications to ensure resident physicians received screening forms before patient encounters. Monthly CRC screening rates were tracked to monitor progress. Results: From January to June 2024, the percentage of patients screened for CRC gradually increased, with a notable spike between March and April 2024. This rise plateaued in May and June, followed by a slight decline through September. The increase was attributed to the new measures, while the plateau and decline were linked to the onboarding of new residents unfamiliar with the EMR (eCW) system and modified workflows. Conclusion: The implemented measures successfully improved the CRC screening rate from 9.3% to 35.28%. However, the target rate has not yet been achieved, and continued efforts are necessary. Future QI projects should address screening rate drops during new resident onboarding.
-

Improving Communication and Follow Up for Incidental Findings from PanScan Imaging
MaKenzie Morrissey, Kristen Payne, Randall Rittmann, Chris Robert, Joseph Lim, and Danielle Pigneri
OBJECTIVE: Incidental findings in medical imaging pose a significant challenge in healthcare due to the potential for missed follow-ups, which can lead to adverse outcomes for patients. These findings, which are unrelated to the primary purpose of the imaging study, are increasingly common due to advances in imaging technology and its widespread use. The consequences of missed follow-ups can be severe. For instance, the rate of malignancy in incidental pulmonary nodule id about 5% and follow up fails in 30-70% of cases. This means for every 120 CT chest scans ordered, 1 lung cancer is missed (McWilliams et al., 2013). One of the challenges contributing to missed follow-ups is the lack of standardized protocols for managing incidental findings. Unlike primary diagnoses, incidental findings do not always trigger immediate action plans, leading to variability in healthcare provider response. The aim of this quality improvement project is to create a standardized method for reporting incidental findings to improve patient follow up. MEATHODS: We reviewed the previous methods for communicating and documenting these findings and developed a new protocol to implement in Medical City Arlington for documentation and discharge follow up instructions. We assessed several “Prior to implementation” trauma patient charts identified patients with incidental findings. We noted how or if these findings were communicated with the patient. We created a standardized method of documenting and communicating incidental findings with MCA Trauma patients including documenting in our progress notes and creating a discharge with follow up order for a physician or IM clinic. We assessed post-study charts to determine adherence to the new standardized documenting method. RESULTS: Project is currently being implemented, and results are pending completion of the project. CONCLUSION: After communication with staff currently documenting and communicating incidental imaging findings we identified areas for improvement, including a need for a standardized method of reporting these findings. The discussions elicited information on successful strategies currently employed that could be enhanced and ideas for standardized reporting methods for the Medical City Arlington Trauma department. Implementation of this project allowed us to better educate patients about their incidentals imaging findings and help ensure patients were provided proper follow up to address these findings. We demonstrated improvement in reporting of incidental findings. With the success of this project, we hope to continue this standardized reporting method at other Medical City facilities.
-

Improving Patients’ Postpartum Contraception Plans and Access to Postpartum Contraception
Rebecca Johnson, Timothy Kremer, and Nicole Tenzel
Introduction: ACOG recommends prenatal discussions with patients regarding their lifetime reproductive plans and postpartum contraception. Up to 40% of patients are not seen for postpartum visits and this rate is highest amongst populations with limited resources (ACOG Practice Bulletin: Optimizing Postpartum Care). By having consistent documentation amongst our clinic providers we aim to maximize patient education and choice in their postpartum contraception. Methods: The providers at our clinic were educated on where to document postpartum contraception discussions on the obstetric flow sheet under the “problems” tab. Providers were to document the discussion even if the patient declined postpartum contraception. Every patient that was seen in our clinic for obstetric care was added to a database and sorted by their estimated delivery date. Patients that were only seen for one visit and thus did not receive prenatal care at our clinic were excluded. The charts of the remaining patients were audited for documentation of a postpartum contraception discussion. If documentation of a postpartum contraception plan was documented anywhere else on the chart this was noted but considered inadequate. Patients were grouped by the month of their EDD and a report was generated for percentage of patients with no documented plan, inadequately documented plan, and adequately documented plan. Results: Data was collected starting with patients with an EDD of July 2023 through April 2024. A total of 203 patients were in the data set. Nine were excluded because they were only seen in the clinic for one visit and did not continue their prenatal care with our clinic. For July through October postpartum contraception plans were still being documented inadequately. By November all contraception plans were documented adequately if any plan was documented at all. The month with the highest percentage of adequately documented plans was in February with 67% of the patients having adequately documented plans. Conclusion: This data shows that we were able to successfully standardize how our providers document prenatal discussions of postpartum contraception. This allows our providers to better identify gaps in care and educate our patients on their contraceptive options. Future areas of study would be to see if consistent documentation leads to higher rates of adequate postpartum contraception.
-

Incidence of Allergic Reactions to Cefazolin in Patients with Penicillin Allergy Undergoing Operative Repair of Pelvis or Extremity Fracture
Hans Drawbert, Laclan Anderson, Marisa Fat, and John Riehl
Introduction Surgical site infections (SSI) account for 20% of all healthcare associated infections with an estimated yearly cost of $3.3 billion in the US alone (1). Cefazolin (Ancef) is a commonly used prophylactic antibiotic in orthopaedic surgery and has been shown to reduce SSI compared to other antibiotics, but potential cross-reactivity in patients with a penicillin allergy (PA) leads to concerns regarding the safety of cefazolin administration. This study evaluates the incidence of allergic reactions to cefazolin in patients undergoing orthopaedic surgery with a PA. Methods A retrospective cross-sectional database review study was conducted. Patients aged 18 or over who underwent operative repair of pelvic or extremity fractures were included. The primary outcome was anaphylaxis or other allergic reaction (defined as skin rash or hives). Logistic regression analysis controlled for variables such as age, sex, race, BMI, and comorbidities. Results 5,823 patients received cefazolin while undergoing orthopaedic surgery (PA: n=354, No allergy: n=5,469). The PA group was found to have an allergic reaction frequency of 2.50% compared to 0.70% in the non-PA group (p=0.0016). The PA group was found to have anaphylaxis frequency of 2.30% versus 0.60% in the non-PA group (p=0.0019), and a skin rash frequency of 0.3% vs 0.1% (p=0.314). Logistic regression revealed odds of allergic reaction are 3.574 times with PA compared to without PA (p-value=0.0004, 95% CI [1.773–7.205]). Conclusion Patients with PA who received cefazolin while undergoing orthopedic procedures had a low likelihood of having any allergic reaction (2.5%). Cefazolin has a different R1 side chain than penicillin and other cephalosporins, and this study confirmed a low cross reactivity in the setting of orthopaedic surgical prophylaxis. Patients with a listed PA are, however, more likely to experience an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis than patients without PA. Because of the broad spectrum gram positive coverage and high bone penetration of cefazolin with a low overall rate of allergic reaction it remains the preferred choice for prophylactic antibiotics in orthopaedic surgery, even in most patients with a listed PA. Patients with a known anaphylactic PA could be considered for treatment with other prophylactic antibiotics.
-

Initiation of Sterile Vaginal Preps Prior to Cesarean Sections: A Quality Improvement Project
Diane Gilbertson, Timothy Kremer, and Kimberly Udell
OBJECTIVE: Research on patients undergoing routine gynecological procedures with a vaginal preparation has demonstrated a significant reduction in post-operative infections by decreasing the burden of vaginal bacteria. Despite this research, as well as evidence that they reduce postpartum endometritis, especially in labor patients or those with ruptured membranes (Lui), vaginal preparations prior to cesarean section are not standard practice. Prior to the initiation of this quality improvement project, no patients delivering at Medical City Arlington received a vaginal preparation prior to a cesarean delivery. The goal of this quality improvement project is to improve clinical care, patient safety, and healthcare operations in the labor and delivery department. METHODS: The patient population was identified, which included (1) established patients of the clinic and (2) patients who are not assigned to an obstetric provider at Medical City Arlington.” Information was then disseminated to all OBGYN residents, attendings, nurses, and operating room support staff explaining the project. The project was conducted from January to April 2024. RESULTS: The total number of cesarean sections completed during the four-month project was N= 57. The total number of cesarean sections where a vaginal prep was applicable was 86% (n= 49). Of the forty-nine applicable cesarean sections, vaginal preps were performed in 49% of cases. The percentage of applicable cesarean sections where a vaginal prep was performed varied over the four-month period, although the rate ultimately increased from 33% to 70% after 4 months. CONCLUSION: In summary, at this institution, vaginal preps prior to cesarean sections are not routine, but this project demonstrated it is possible to institute this practice. If the initiation of vaginal preps can reproduce past studies in the reduction of postpartum endometritis, it would provide further evidence that obstetricians should adopt the implementation of vaginal preps at the time of cesarean section as the standard of care.
-
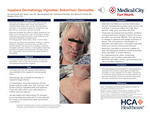
Inpatient Dermatology Vignettes: Seborrheic Dermatitis
Garrett Furth, Henry Lim, Marshall Hall, Christian Scheufele, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory disorder characterized by greasy scale, itching, and erythema. It commonly affects areas of the skin that have high sebum production or are sebaceous gland-rich, including the scalp, face, sternum, axilla, groin, and other skin folds. Seborrheic dermatitis can present in infants, adolescents, and adults, and is more common in men. The etiology is not fully understood, but contributing factors include presence of the yeast genus Malassezia, androgen levels, immunosuppression, family history, and stress or lack of sleep. Interestingly, those with neurological and psychiatric conditions, including Parkinsons Disease, spinal cord injury, epilepsy, and tardive dyskinesia, are often more severely affected. This may be due to changes in dopamine and greater production of sebum. In these patients, seborrheic dermatitis can present more extensively, with larger salmon-pink, scaly plaques, some of which can even appear petaloid or ring shaped. Awareness of seborrheic dermatitis is important as every primary care clinician will see patients with this common disorder. Efficient identification can expedite proper therapy and reduce symptoms, while education can alleviate psychological distress. Common mimicking diagnoses include psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, tinea infections, and pityriasis rosea. The presented case was a hospital consultation for psoriasis vs extensive fungal infection, in a patient with severe cervical spinal stenosis. Case Presentation: A 64-year-old man with severe spinal stenosis was admitted to the hospital for cervical spinal fusion. Dermatology was consulted for psoriasis vs extensive fungal infection. On examination, there was erythema with fine greasy scaling to scalp, face, and ears, with thicker scaling to nasolabial folds and eyebrows. There were also salmon-pink scaly plaques to chest and sternum. He was treated with ketoconazole 2% shampoo, as he was being treated with also being treated with IV corticosteroids per surgery, and experienced rapid improvement in symptoms. Learning points: We share this case demonstrating a case of seborrheic dermatitis in a patient with severe spinal stenosis. Physical exam findings revealed salmon-pink plaques to chest and sternum, with erythema and fine greasy scaling to face, scalp and ears, with thicker scaling in nasolabial folds and eyebrows. This case highlights the importance of understanding the distribution and conditions associated with seborrheic dermatitis, as many other diseases can be easily confused for it. All primary care physicians will encounter patients with seborrheic dermatitis and they should take these points into great consideration when diagnosing patients.
-

Investigating the Relationship Between Skin Color, Ethnicity, and the Fitzpatrick Skin Scale
Henry Lim, Dana Olsen, Reem Ayoub, Maria Francesca Ysabelle Martinez, Rafael do Valle, Kristina Kafle, Christina Guo, Marshall Hall, Christian Scheufele, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Introduction: The Fitzpatrick skin scale has long been used as a proxy for skin tone categorization. However, its initial creation was to classify reactivity of white skin to ultraviolet A radiation. A reported one-third of dermatologists conflate the Fitzpatrick skin scale for race and ethnicity. Approximately half of the dermatologists also reported utilizing the Fitzpatrick scale to describe skin color. The goal of this study was to compare the Fitzpatrick scale to skin color and ethnicity in a larger, cohort including the full spectrum of skin tones. Methods: Subjects completed a standardized questionnaire. The questionnaire encompassed subjective classification methods: self-reported skin color descriptors (very fair, fair, olive, light brown, dark brown, and very dark), self-assessed Fitzpatrick skin type (I-VI) and ethnicity. The questionnaire included the following ethnicities: White, Asian, African American or Black, Hispanic or Latino, Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, Multiple Ethnicities, and Other. If more than one ethnicity was chosen, the subject was reported as “multiple ethnicities.” Chi-squared tests were performed comparing skin color and ethnicity to Fitzpatrick skin type. Results: 440 subjects completed the questionnaire. Chi squared test revealed that each Fitzpatrick type was composed of significantly different proportions of skin colors (p < 2.2e-16). There was a weak association between Fitzpatrick type and self‐described skin color (Cramér’s V=0.3). While there is a significant difference in the percentage of each ethnicity found in each Fitzpatrick type (p < 2.2e-16), each ethnicity could not be modeled off individual Fitzpatrick types. There was representation from all ethnicities in each Fitzpatrick type. There was a weak association between Fitzpatrick-type and ethnicity (Cramér’s V=0.3). Conclusion: This study confirms previously cited flaws of the Fitzpatrick scale. Our study found no statistically significant proportion of a singular skin color descriptor or ethnicity within each Fitzpatrick skin type. This serves as emphasis that there is no relationship between physical traits or cultural identity with the Fitzpatrick scale.
-

Isolated Unilateral Medial Rectus Palsy Due to Acute Pontine Infarction
Miranda Bingham, Shterna Frand, Charley Meadows, and Sanjay Sharma
Isolated unilateral medial rectus palsy is a rare but significant clinical manifestation of acute pontine infarction, often presenting without the typical neurological deficits seen in brainstem strokes. This case report highlights a 61-year-old male with a history of hypertension and diabetes who presented with four days of double vision, with no other significant neurological symptoms such as headache, speech disturbances, or focal weakness. On examination, the patient exhibited an isolated inability to adduct his left eye, without any visual deficits or abnormalities in other cranial nerve functions. Neuroimaging, specifically MRI, confirmed the diagnosis of an acute left pontine infarction. The medial rectus muscle, which facilitates eye adduction, is innervated by the oculomotor nerve and its function is coordinated by the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF). Lesions affecting the MLF, often due to pontine strokes, can result in isolated medial rectus palsy, a condition that may be challenging to diagnose, especially when no other oculomotor deficits are present. This case underscores the importance of considering acute stroke in the differential diagnosis when encountering isolated ocular motor abnormalities, particularly in patients with risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes. Early neuroimaging is essential for confirming the diagnosis of pontine infarction, distinguishing it from other potential causes of eye movement abnormalities, such as demyelinating diseases or mechanical injuries. The timely recognition of such conditions is critical, as it allows for appropriate intervention and management to reduce the risk of long-term deficits. Furthermore, this case emphasizes the need for a multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, ophthalmologists, and rehabilitation specialists to optimize patient care. With early diagnosis and management, some patients may experience partial or complete recovery of eye movement, while others may require ongoing rehabilitation to address residual deficits.
-

Laproscopic Robotic-Assisted Common Bile Duct Exploration for Primary Choledochlithiasis 20 Years After Cholecystetomy in a Hostile Abdomen
Enoch Wong, Kristen Payne, James Burdick, and Hassan Ahmed
Introduction: The incidence of concomitant cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis is 5-20%. Primary choledochlithiasis more than 3 years after cholecystectomy is an even rarer event with only a handful of case reports in the literature. Robot-assisted laparoscopic common bile duct exploration with intraoperative choledochoscopy is a relatively recent development in biliary surgery. In this report, we describe the use of this technique in a patient with rare presentation and surgically challenging anatomy. Objective: To describe a minimally invasive approach for CBD exploration with extraction of choledocholithiasis in a surgically hostile abdomen and Roux-En-Y anatomy. Methods: This report describes the case of a 60 year old male with extensive surgical history including open right colectomy with cholecystectomy, distal gastrectomy for perforated ulcer with Roux-En-Y gastrojejunostomy, and additional multiple exploratory laparotomies with large and small bowel resections, and a final surgery with end ileostomy creation. He presented to our facility with ascending cholangitis secondary to choledocholithiasis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirmed 2 CBD stones. An advanced gastroenterologist attempted Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with a pediatric scope, single and double balloon enteroscopy without success to reach the ampulla of Vater. We present this case as a video presentation using intraoperative footage to describe the technique used. Results: After extensive enterolysis, two large CBD stones were removed under direct visualization without any residual choledocholithiasis. The choledochotomy was closed primarily and the patient was discharged without complications. Conclusion: We are reporting a rare case of primary choledochlithiasis after more than 20 years of cholecystectomy in a patient with Roux-En-Y anatomy and very hostile abdomen using a minimally invasive approach with uneventful recovery. Based on our experience with this case, we believe that this procedure provides a promising option for treatment of choledocholithiasis that is refractory to other interventions or in patients with challenging anatomy.
-

Lessons Learned: A Multicenter Approach to a Mass-Casualty Incident
Kristen Payne, Elizabeth Kim, Luis Taveras, Morgan Collom, and Danielle Pigneri
Background: On May 6, 2023, an armed gunman opened fire at a shopping mall in Allen, Texas. Eight people including the perpetrator were killed with more injured. Medical City McKinney, a level 2 trauma center received seven patients. Medical City Plano, a level one trauma center received one patient. Medical City Dallas Children’s Hospital, a level three pediatric trauma center received one pediatric patient. Methods: Medical City North Texas Division command center engaged Emergency Department leadership at North Texas facilities to prepare for transfer of patients. Ground transport and an air medic team on standby was staged early on. Nearby non-trauma centers sent available staff for support. Results: Small group debriefs occurred with team leaders, followed by a larger internal debrief. Debriefs were also conducted externally with division leadership, Medical City Dallas Children’s Hospital, Medical City Plano, and the North Texas Transfer Center. The lessons learned have been divided into five categories: 1. Communication: • Official communication of the MCI plan via an overhead alert and call to leadership. • The development of a succinct MCI Response Plan Checklist. • An emergency contact number for the Medical Examiner. 2. Roles and Responsibilities: • The command center was established which expedited the labor pool, patient tracking, and the Family Reunification Center. • An ER RN staged at the EMS bay functioned as the Triage Unit Leader. 3. Mobilization of Resources: • Mobilization of staff allowed for more extensive care without depleting resources. • Early allocation of pediatric transportation prevented delays in care. • Environmental Services was needed to manage turnover of the trauma rooms. 4. Safety, Security and Forensics: • Forensic training is essential and continued education should be available. • A set of ID badges should be available for emergent staff access. 5. Clinical Care and Support of the Patient and Staff: • Recovery of the surgery schedule took several days. • The behavioral health team provided PTSD and depression care early • Rehabilitation physicians provided early evaluations and facilitated the transition from hospitalization, rehabilitation, and eventually home for patients and their families. Conclusions: Further development of tabletop exercises, mock MCI drills, additional education for staff, frequent review of the MCI Response Plan Checklist, and implementation of additional protocols are anticipated. It is imperative major trauma facilities remain prepared for mass casualty incidents with strong protocols, regular drills, behavioral health and rehabilitation support, and thorough local and regional debriefs.
-

Lost Work Due To Burn Related Disability In A US Working Population
Hannan A. Maqsood, Zhaohui Fan, Naveen F. Sangji, and Danielle Pigneri
Introduction: Burn injuries can require hospitalization, operations, and long-term reconstruction. Burn-injured patients can experience short- or long-term disability. We investigated lost workdays (LWDs), short-term disability (STD), and long-term disability (LTD) in the 12-month period following a burn injury. Methods: An observational cohort study was conducted using a commercial claims database, IBM® MarketScan®. Patients aged ≤65 years with an ICD-10 burn diagnosis from 2018 to 2019 were included. The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), procedure and Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes were used to identify patients undergoing burn-related operations. Patients were mapped to data tables for LWDs, STD, and LTD for the 12 months pre- and post-injury. Paired t-tests were employed to compare the pre- and post-injury outcomes. Results: We identified 1745 patients with burn diagnoses. Of those, 263, 1449, and 1448 patients had data available for LWDs, STD, and LTD, respectively. STD and LTD were reported by 8.1% and 0.0% of patients in the 12-month period pre-injury, respectively, and 20.3% and 1.0% of patients in the 12-month period post-injury, respectively. Average days of STD increased from 3.70 to 9.34 days following injury. Conclusions: Burn injuries are associated with increased STD and LTD utilization. Quantifying the impact of burn injuries on patients’ work will help us understand the economic implications of burns, which is a key area in burn research.
-

Malignant Phyllodes Tumor with Osteosarcomatous Differentiation
Chris Robert, Kayla McCarthy, and Danielle Pigneri
Introduction: Phyllodes tumors are fibroepithelial tumors accounting for 1% of primary breast neoplasm with malignant transformations occurring in 10-20% of the tumors. Heterologous osteosarcomatous differentiation is a rare and aggressive variant associated with poor prognosis. Case report: A 38-year-old female presented with a mass that she noticed a month ago with increase in size of mass to 10cm at time of presentation. A biopsy of the mass showed a fibroepithelial lesion with focal areas of stromal overgrowth, accompanied by stromal hypercellularity without evidence of nuclear pleomorphism, mitotic activity, necrosis and heterogenous elements most likely a benign phyllodes tumor. Due to discordance with clinical examination, and large size of tumor she underwent a mastectomy a month after presentation, in the interim period the tumor had grown to 20cm, with the appearance of cystic structures anteriorly. A skin sparing nipple sparing mastectomy was performed, carefully preserving and excising the cystic structure anteriorly. The specimen weighed 950gm.This was followed by an autologous reconstruction with a deep inferior epigastric perforator flap. The following day patient was noted to have venous congestion of the flap and she returned to the operating room for exploration of the flap and an interposition vein graft was performed to revascularize the venous component to a secondary lateral venae comitante of the inferior pedicle. Patient was discharged home the next day. The pathology returned malignant phyllodes tumor with heterologous osteosarcomatous differentiation, pleomorphic stromal cells, increased mitotic activity, all margins free by 0.1cm or less (Fig 1). Patient was taken back to the operating room a month later for reexcision partial mastectomy for margins. This was followed by removal of flap and flat reconstruction. Pathology showed residual malignant phyllodes, nipple and skin negative for involvement and margins negative by 0.2cm or more.Patient did well postoperatively and is currently undergoing radiotherapy Learning point: Phyllodes tumors are fibroepithelial categorized as benign, borderline or malignant based on tumor margins , mitotic activity and stromal cellularity, atypia and overgrowth. A tumor with infiltrative margins, atypia, mitotic activity of >10 per 10hpf, stromal hypercellularity and overgrowth is characterized as a malignant phyllodes tumor. Presence of heterologous sarcomatous differentiation such as liposarcoma, chondrosarcoma or osteosarcoma also indicate malignant transformation. Definitive treatment involves wide surgical excision or mastectomy depending on the size of the tumor. Malignant phyllodes have local recurrence rates ranging from 23 -30%. Studies have shown those with a large tumor and heterologous osteosarcomatous differentiation have greater risk of developing distant metastasis. These tumors spread hematogenously, hence axillary lymph node dissection is not generally indicated. Some studies recommend adjuvant radiation in patient with tumors greater then 5cm and more than 20 mitosis/hpf because of high local recurrence rates.
-
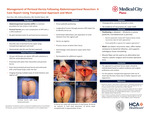
Management of Perineal Hernia Following Abdominoperineal Resection: A Case Report Using Transperineal Repair and Mesh
Evan Chen, Anthony Macaluso, and Danielle Pigneri
Background & Significance: Abdominoperineal resection (APR) is a complex surgical procedure commonly performed for low rectal or anal cancer. A rare complication following this surgery is the development of perineal hernias, occurring in 1-26% of cases. There is no universally accepted treatment for perineal hernias, and management is often individualized. Treatment options include conservative measures, transabdominal versus transperineal repair, varying patient positioning, and the use of mesh. This case report describes a transperineal repair in a prone jack-knife position using mesh for pelvic floor reconstruction. Case Presentation: A 54-year-old female status post robotic APR for rectal adenocarcinoma presented with symptomatic perineal hernia. Physical examination revealed small bowel loops protruding under the skin, confirming the hernia and enterocele. The patient was placed in a prone jack-knife position and a longitudinal incision was made through the previous APR staple line. The hernia sac was identified with small bowel protrusion. After adhesiolysis, the hernia sac was ligated without damage to the intestine. The pelvic floor fascia was closed and ACell biologic mesh was placed to repair the pelvic floor defect. Perineoplasty provided additional support, followed by closure of the deep subcutaneous tissue and skin. Discussion: The transperineal approach with prone jack-knife positioning was chosen for optimal visualization of the hernia and surrounding structures. A systematic review of perineal hernia repairs suggests that both perineal and abdominal approaches have similar recurrence rates, but the perineal approach was preferred for this patient. Mesh repair has been associated with lower recurrence rates compared to non-mesh repair and offers benefits such as reduced bacterial infection risk and better integration into irradiated tissue. This case emphasizes transperineal approach as a preferred treatment option but also highlights the importance of tailoring the surgical approach to the patient's anatomy and the surgeon's expertise.
-
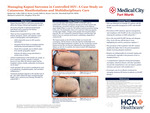
Managing Kaposi Sarcoma in Controlled HIV: A Case Study on Cutaneous Manifestations and Multidisciplinary Care
Rafael do Valle, Reem Ayoub, Henry Lim, Marshall Hall, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Introduction: Kaposi Sarcoma (KS) is a soft tissue sarcoma that affects the linings of blood and lymphatic vessels. It occurs, primarily in immunocompromised individuals. It is caused by the Human Herpesvirus 8. There are four recognized forms of KS: AIDS-related, iatrogenic, classic, and endemic. Each form varies in demographics and manifestation. AIDS-related KS occurs in HIV-positive individuals, while iatrogenic KS develops in transplant patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy. Classic KS is typically seen in elderly males from specific geographic regions, and endemic KS affects young individuals in certain areas of Africa. Clinical manifestations of KS include red, purple, or brown papules or plaques. In addition, Kaposi's sarcoma can affect all visceral organs and the lymphatic system; notably, pulmonary involvement can be fatal. If left untreated, KS can lead to complications such as lymphedema, lymphadenopathy, and secondary malignancies. Treatment strategies depend on the specific type of KS, with AIDS-related KS often managed through Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) to control HIV.
-

Maternal Cardiovascular Risk and Lactation: Disparities and Future Directions
Monica Rodriguez, Michele McCarroll, Caroline Marrs, and Kamala P. Tamirisa
Pregnancy functions as a cardiopulmonary stress test, unmasking underlying cardiovascular disease (CVD) or heightening the future CVD risk following adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs). Multiple studies have demonstrated strong associations between APOs, higher mortality rates, and an increased risk of cardiometabolic diseases. Black women, in particular, have a disproportionately higher burden of coronary artery disease related mortality, with an earlier onset compared to women of other racial and ethnic groups. Increasing allostatic load due to both acute and chronic racial discrimination may potentially be a key factor driving poorer pregnancy outcomes. Breastfeeding has a protective effect on allostatic load and is linked to improved maternal cardiometabolic health In the United States, Underrepresented Racial and Ethnic Groups (UREG) have the lowest rates of breastfeeding initiation, retention, and duration—potentially influenced by both cultural factors and systemic biases within healthcare. Interventions must extend beyond healthcare settings to engage key stakeholders, including community leaders and families to create sustainable change and reduce disparities. As maternal CVD prevalence rises among UREG populations, a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach to improving breastfeeding rates is essential to improving maternal and infant health outcomes.
-

Mimicking Malignancy: A Case of Non-Traumatic Myositis Ossificans in the Calf
Fatima Safi, Artur Amirkhanyan, Amnah Andrabi, and Madeline Doucet
Objective: This case report highlights the diagnostic challenges of non-traumatic myositis ossificans (MO), a rare benign heterotopic ossifying lesion, and emphasizes its potential to mimic malignancy. Case Presentation: An 18-year-old female with no trauma history presented with a one-month history of progressive right calf pain, ankle weakness (4/5 strength), and difficulty ambulating. Initial ultrasound suggested a hematoma, but the persistence of symptoms prompted advanced imaging. CTA revealed arterial extravasation, while MRI identified a heterogeneously enhancing soleus muscle mass, raising suspicion for sarcoma. Core biopsy demonstrated focal bone formation, mitotically active stroma, and a "zone phenomenon" (central cellularity with peripheral osteoid maturation), pathognomonic for MO. Results: Histopathology confirmed non-traumatic MO, avoiding unnecessary interventions. The absence of trauma, atypical soleus involvement, and imaging overlap with sarcoma underscored diagnostic complexity. Multidisciplinary collaboration (vascular surgery, radiology, orthopedics) and biopsy were critical to exclude malignancy. Conclusion: Non-traumatic MO, though rare, should be considered in soft-tissue masses regardless of trauma history. Early histologic evaluation is essential to differentiate it from sarcoma and prevent iatrogenic harm. This case underscores the importance of recognizing MO’s variable presentation and the role of multidisciplinary teamwork in guiding conservative management. Further research is needed to elucidate the incidence and pathophysiology of idiopathic MO.
-
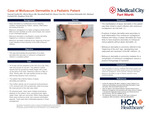
Molluscum Dermatitis in a Pediatric Patient
Garrett Furth, Olivia Mayer, Marshall Hall, Henry Lim, Christian Scheufele, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic relapsing condition characterized by irritation, redness, inflammation, and itching of the skin. The cause of AD is theorized to be multifactorial, including genetic components, such as mutations in filaggrin, environmental exposures, and immune predisposition. AD often presents in childhood and adolescence, but can appear at any age. AD eruptions arise through various triggers, which commonly include soaps, detergents, fabrics, and cold or hot weather. Importantly, viral infections can also serve as a trigger, causing systemic inflammation via host defense mechanisms. Molluscum contagiosum (MC) is a double-stranded DNA virus that classically manifests as small, dome-shaped, skin-colored to pink, umbilicated papules. MC is very common, highly contagious, and often spreads via direct person to person contact. It can also spread from an affected to unaffected area of the body through autoinoculation. Molluscum dermatitis is the manifestation of an AD episode, triggered by MC. Patients with a history of atopic dermatitis are more likely to have eruptions associated with MC lesions. Interestingly, molluscum dermatitis is deemed the “beginning of the end” (BOTE), a positive finding indicative of host mechanisms working to resolve MC infection. We share this case as a presentation of AD flare secondary to molluscum contagiosum infection in a pediatric patient. Case Presentation: An 8 year-old boy with family history of atopic dermatitis presented with parents for red itchy rash and bumps. Patient’s mother reported that symptoms initially began with a rash on the back of the patient's neck, following a haircut in May 2024. Shortly afterwards, this rash began to spread across his body, with bumps becoming more numerous. He was intermittently treated with hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment (brother’s prescription) with mild symptomatic relief, but without improvement in rash. On examination, there were eczematous plaques on the anterior neck, supraclavicular region, upper chest, right arm, and axilla. Within these plaques were numerous small skin-colored umbilicated papules, some in a linear arrangement. Learning points: We share this case demonstrating molluscum dermatitis in a pediatric patient. The manifestation of AD in this patient was likely directly linked to recent infection with MC, due to systemic inflammation caused by viral load, thus subsequently causing the eruption. Molluscum dermatitis is often referred to as the “beginning of the end” (BOTE) sign and represents host responses preceding the resolution of MC infection. Molluscum dermatitis is commonly mistaken for a complication of MC, and all physicians should take this point into consideration when diagnosing patients.
-
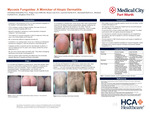
Mycosis Fungoides: A Mimicker of Atopic Dermatitis
Christian Scheufele, Paige Loux, Henry Lim, Garrett Furth, Marshall Hall, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Introduction Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a rare, cutaneous, malignant neoplasm of the resident T cell lymphocytes within the skin. CTCL encompasses a spectrum of morphologically and prognostically distinct entities, the most common of which is mycosis fungoides (MF). The incidence of mycosis fungoides is about 6 cases per million per year in the United States and Europe. MF is notoriously difficult to diagnose clinically. It can masquerade as several common dermatologic conditions and may be treated as such for years until a biopsy reveals the correct diagnosis. One of the most common diseases that MF mimics is atopic dermatitis (AD). Severe atopic dermatitis and MF share overlapping distributions and similar morphologies. Here we present cases illustrating the differences and similarities between Mycosis Fungoides and Atopic Dermatitis. Case Presentation A 54-year-old Fitzpatrick II (mostly burns, rarely tans) female demonstrates patch/plaque stage mycosis fungoides shown in Figure 1. There are pink to erythematous patches and thin plaques in non-sun-exposed areas, known as a “bathing suit” distribution. There is also notable poikiloderma with hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, skin atrophy, and telangiectasias. In Figure 2, a Fitzpatrick VI (never burns, always tans) male displays erythrodermic mycosis fungoides. There is generalized erythema with diffuse overlying hyperkeratotic papules coalescing into scaly plaques. Figure 3 shows a 38-year-old Fitzpatrick IV (rarely burns, mostly tans) male with chronic atopic dermatitis and secondary lichen simplex chronicus. There are lichenified plaques with overlying linear erosions suggestive of scratching. Learning Points MF classically presents as hyper and hypopigmented mottled patches or plaques with telangiectasias involving atrophic skin. The rash is caused by a clonal population of atypical, malignant T cell lymphocytes. It presents in sun spared areas, known as a “bathing suit distribution” because the malignant T cells are sensitive to ultraviolet light. In the early stages, the skin may appear xerotic, or dry and flaky. This makes active areas of MF difficult to distinguish from normal skin or atopic dermatitis. AD is much more common, affecting approximately 7 % of adults in the United States. It classically begins in childhood and can involve the hands, feet, trunk and flexural surfaces. It typically presents as dry, erythematous to hyperpigmented plaques with or without lichenification. It is important to consider mycosis fungoides in the differential diagnoses for any longstanding eczematous rash that is resistant to common therapies for atopic dermatitis and clinical suspicion should prompt a skin biopsy.
-
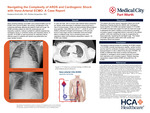
Navigating the Complexity of ARDS and Cardiogenic Shock with Veno-Arterial ECMO: A Case Report
Sanjana Kesireddy and Mohan Sengodan
INTRODUCTION: When deciding between VA ECMO (veno-arterial ECMO) and VV ECMO (veno-venous ECMO), the primary consideration is the underlying pathology affecting the patient’s heart and lungs. VA ECMO provides support for both the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, making it suitable for patients experiencing cardiogenic shock or combined cardiac and respiratory failure. In contrast, VV ECMO is used exclusively for respiratory failure, offering support to patients with severe lung dysfunction but intact cardiac function. CASE PRESENTATION: 41 year old male with no known past medical history presented s/p cardiac arrest secondary to aspiration pneumonia due to alcohol and opioid intoxication. Chest xray demonstrated diffuse bilateral lung opacities. Initial ABG had a pH of 7.1, pCO2 55, pO2 57. Patient underwent emergent bronchoscopy in ED and was found to have large volume of aspirated vomit and foreign debris in bilateral lungs. Due to worsening lactic acid, respiratory status and increasing vasopressor support, VA ECMO was initiated. LEARNING POINTS: This patient had acute hypoxic respiratory failure and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) with Cardiogenic shock therefore VA ECMO was started instead of VV ECMO. VA ECMO provides dual support for both the heart and lungs. It addresses the heart's inability to pump blood by providing circulatory support (oxygenated blood is returned to the arterial system), while also assisting the lungs by oxygenating the blood externally, bypassing the damaged lungs. This makes VA ECMO particularly useful when both cardiac and respiratory failure are present.
-

Necrotizing Alternaria Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Male
Joel Mathews, Jose Aguilar-Martinez, Sean Sojdie, Zain Tariq, and Tamer Hudali
Abstract: Alternaria species is a rare cause of invasive fungal pneumonia, typically described as an opportunistic pathogen, usually seen in immunocompromised patients producing virulent forms of sinus, cutaneous, and ocular infections. Alternaria species sparingly affect immunocompetent individuals and are often managed without any medical interventions. We present a case of invasive fungal necrotizing pneumonia caused by Alternaria alternata species in an immunocompetent 28-year-old male with only a past medical history of well-controlled asthma managed with an as-needed albuterol inhaler. His complaints included worsening foul-smelling productive cough with yellow-dark brown sputum along with subjective fevers, chills, chest pain, and dyspnea for one month. His occupation involved weeding deer fields which involved exposure to dust particles. He reports not using a mask or other protective equipment. He denied recent travel, bird exposure, history of covid infection or family history of malignancy. He initially presented to outside facilities and was started on empiric oral antibiotics like doxycycline and augmentin, however, after failing outpatient therapy, he was referred to a pulmonologist. The pulmonologist ordered a CT chest which revealed a right lower lobe consolidation with cavitation mass. He subsequently underwent bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsies that were surprisingly negative for malignancy or bacterial infection. During this time, HIV and hepatitis testing along with Interferon Gold testing were performed and were all negative, but patient’s symptoms worsened despite antibiotic therapy in addition to systemic steroids, and as a result, he was admitted to the hospital for further evaluation and management. Patient’s serum IgE level was obtained prior to admission and was found to be elevated at 3000. Fungitell and galactomannan were also significantly elevated. A CT angiogram of the chest obtained during this hospital admission revealed significant progression of right lower lobe consolidation with bronchiectatic changes. Fungal cultures of outpatient bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) from the bronchoscopy returned positive for Alternaria alternata species. After conferring with pulmonology and infectious disease specialists, the patient was eventually transitioned to intravenous itraconazole along with systemic steroids demonstrated significant clinical improvement and was stabilized for discharge with proper outpatient follow up with pulmonology, infectious disease, and primary care. Althought IgE levels were elevated, a thorough auto-immune workup was obtained and was negative for any auto-immune conditions such as sjogren's disease, systemic lupus erythromatosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, and more. Our case highlights the importance of considering occupational hazards in the management of atypical pulmonary pathology in an immunocompetent male. Case Description: Medical History: The patient is a 28 year-old male with past medical history of asthma admitted for sepsis secondary to persistent pneumonia concerning for invasive necrotizing fungal pneumonia. Patient reports the onset of productive cough with malodorous yellow-brown sputum for about one month prior to admission. Patient initially presented to an outside emergency department (ED), where a CT chest was obtained and showed a 4.0 cm mass-like opacity in the basal segment of the right lower lobe of the patient’s lung, patient was discharged on oral doxycycline, as the patient was suspected to have a typical lobar pneumonia from a bacterial infection. Patient’s symptoms did not improve after completing the antibiotic course, and he presented to another outside ED where another CT chest was obtained and showed the same right lower lobe mass, however, it increased in size to 4.2 cm. The patient was then started on oral augmentin and re-presented to his primary care provider who referred him to pulmonology who ordered a repeat CT chest revealing a cavitary right lung mass. Patient underwent bronchoscopy where large mucus plug was identified and transbronchial biopsies obtained were negative for malignancy or bacterial infection. Outpatient HIV/hep/quantiferon gold testing was negative. Serum IgE levels were ordered and were approximately 3,000. Fungal culture from bronchoalveolar lavage were positive for Alternaria. Patient had been on empiric antibiotics for 4 weeks with worsening dyspnea, subjective fever, and chills. On admission, patient was hemodynamically stable. A CT angiogram of chest showed significant progression of right lower lobe cavitation consolidation with bronchiectatic changes. Patient also reported acid reflux-related symptoms with post-tussive emesis and GI was consulted. Infectious Disease was consulted for antifungal assistance. Infectious Disease History: Patient has a history of asthma well controlled with as-needed inhaled albuterol, with only 4 episodes of severe asthma exacerbations requiring steroids four times annually. Patient reports no bird exposure. Patient reports annual cleaning of deer lease areas with weeding leading to dust dispersal into the air, and during these episodes he does not wear a mask or other protective equipment. After an episode of dust exposure, he began developing worsening symptoms. At baseline, he makes balls of brown foul-smelling sputum frequent, especially in the past two years and recently began getting worse. During this period, he denies any hemoptysis, but admits to frequent vomiting secondary to developing gastroesophageal reflux disease from nocturnal coughing spasms in addition to night sweats. Patient presented to an outside emergency department twice and was started on empiric antibiotics which did not improve symptoms, and was eventually referred to a pulmonologist who ordered a CT chest which revealed right lower lobe consolidation with cavitation mass. He subsequently underwent bronchoscopy which he was noted to have partial narrowing and obstruction of the superior segment of right lower lobe of lung. Transbronchial biopsies that were negative for malignancy or bacterial infection; broncho-alveolar lavage (BAL) samples were obtained and eventually were positive for Alternaria alternata species. He was also tested for HIV and hepatitis along with Interferon Gold testing for tuberculosis (TB), all of which were negative. Patient also had an IgE level obtained which was elevated at 3000. Despite the elevated immune marker, laboratory testing at MCFW revealed negative titers for auto-immune conditions such as Sjogren's disease, scleroderma, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) although anti-CCP titers were elevated. When patient’s symptoms continued to persist despite empiric antibiotics, steroids, and inhalers, he was admitted to the hospital for further evaluation. He was started on intravenous vancomycin, cefepime, and eventually itraconazole, and oral steroids were discontinued. After BAL cultures were positive for Alternaria alternata, the the patient was continued on these antibiotics and antifungals and discharged on intravenous antibiotics with close outpatient follow-ups to his pulmonologist, infectious disease specialist, and primary care doctor, demonstrating significant clinical improvement. Discussion: Our case involved an immunocompetent young male with a known history of asthma who was admitted for persistent pneumonia. Outpatient bronchoscopy results revealed a fungal pneumonia with Alternaria species. Alternaria species are increasingly found to be the etiology of fungal sinus, pulmonary, and central nervous system disease in transplant and leukemic patients. The incidence of Alternaria pneumonia is not well documented given the challenge of diagnosis.
-

NFL Kick-off Rule Change: A Comparative Analysis of Injury Incidence
Troy Puga, Tanner Haechten, Coleman Cush, McKenna Box, Hans Drawbert, and John Riehl
Introduction: Kickoffs in the National Football League (NFL) remain one of the most dangerous plays during an NFL game, with high levels of injuries. In 2024, the NFL implemented kickoff rules intended to reduce the number of injuries during this play, and improve player safety. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of the 2024 NFL kickoff rules on the incidence of injuries during the kickoff. Methods Injuries on kickoffs were identified for the 2024, 2023, and 2022 NFL seasons using the transcribed game book for each game on the official NFL website. Injury type was confirmed using the injury report on each individual teams website for the following week. If an injury was unreported on the subsequent injury report, it was listed as an unspecified injury. Injury rate was calculated for each injury category during each year using average game exposure. The incidence rate ratio was calculated by dividing the IRR of one season over the other season. 95% confidence intervals were calculated for the IRR and a z-test for proportions was used to test for significance. Results Comparison of the 2024 versus 2022 season showed no statistically significant difference (P>.05) in the number of overall injuries, concussions, or subcategory of injuries. When compared with the 2023 NFL season, the 2024 NFL season showed a statistically significant rise in lower extremity injuries during the 2024 NFL season (P=0.048), but no statistically significant difference (P>.05) in the number of overall injuries, concussions, or remainder of subcategory injuries. When the 2023 and 2022 NFL seasons were compared, there was no statistically significant difference (P>.05) in the number of overall injuries, concussions or additional subcategories. Conclusions After the 2024 NFL kickoff rules were implemented, there was no improvement in decreasing the level of injuries that players experienced on kickoffs when compared with the two prior seasons. The kickoff remains a dangerous play with high levels of injuries, and the NFL should continue to evaluate potential rule changes to improve the safety of players during this play.
-

Optimization of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis in Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period
Sereena Jivraj, Isabella Sciacca, Sherrie Dixon, and Timothy Kremer
Background: Venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolisms (PE) continues to be a leading cause of maternal mortality (MM) in the United States. VTE accounts for roughly 9-10% of all maternal deaths. Other countries have adopted anticoagulation protocols to reduce MM rates, but the US has yet to follow suit. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST), and the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) all vary in their guidelines for thromboembolism prophylaxis. Patients who deliver by Cesarean section (C-section) have higher incidences of MM due to pulmonary embolism. Specifically for patients who undergo a C-section, ACOG recommends only mechanical compression devices along with a risk scoring system, which is not standardized across hospitals. Objective: Improve existing data regarding populations at risk for VTE consequences; Create a standard practice across the nation for anticoagulation in those with increased risk of MM due to VTE. Methods: Develop a QI project in order to establish a protocol and track outcomes. Perform a retrospective analysis of patients with these risk factors (listed below) within our Graduate Medical Education (GME) population to determine our pre-protocol VTE risk at Medical City Women’s Clinic. Create a protocol in which high-risk patients receive low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) for VTE prophylaxis. Track outcomes and compare VTE risk in this cohort compared to our population baseline Eventually expand to other institutions to improve the power of the study and MM rates amongst the general public in the United States. Risk Factors: Pre-eclampsia diagnosis Cesarean section Postpartum hemorrhage Postpartum infection such as endometritis BMI > 30 Personal history of thrombosis Multiple gestation Anticipated Results: We anticipate that with this protocol, patients will experience reduced rates of VTE consequences in the postpartum period. We also anticipate that with a strong enough study, our findings would allow us to make a case for standardized VTE prophylaxis guidelines by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).
-

Optimizing Fluid Resuscitation: Balancing Access efficiency and Infusion Speed in Trauma care
Chris Robert, Enoch Wong, David Bassa, Danielle Pigneri, and Paul Granet
Study Objective: Time is a critical resource during the initial treatment of an injured patient. Fluid resuscitation is also a critical component of trauma care. Clinicians are faced with the need to actively resuscitate an injured patient while simultaneously working to provide them operative or procedural hemorrhage control as quickly as possible. In these circumstances, physicians must balance perceived flow efficiency with time required to place certain types of access devices, though little data exists to guide this decision process. This study aims to evaluate the infusion times of different sizes of peripheral and central venous catheters to optimize fluid administration in emergency settings. Design & Methods: This is an experimental study assessing fluid infusion times across various peripheral and central venous access devices. To eliminate extraneous influence, infusion times by gravity alone were compared across catheter types. We measured the time required to infuse crystalloid fluid (Lactated Ringer’s solution) through different cannula and catheter sizes. The infusion was performed in a standardized manner using gravity flow, with the fluid bag placed at a height of 3.5 feet from the catheter. The completion time for one liter of fluid to drain by gravity was recorded independently by two observers. Results: While an increase in catheter size generally correlated with improved flow rates, notable variations were observed between peripheral and central venous access devices. The study found that while 14G and 16G cannulas outperformed 18G in terms of infusion times, the 16G demonstrated a marginal advantage over a 9 Fr Cordis catheter. The findings are presented in the table below. Catheter gauge/Fr Time (seconds) 14G 456 16G 534 18G 785 20G 1174 Triple lumen 7Fr 1675 Cordis 9Fr 544 Conclusion: Understanding the flow time of various intravenous access devices is essential to making timely clinical decisions for fluid resuscitation in trauma patients. Based on our data, the time required to place a Cordis catheter is not justified for volume resuscitation alone if the patient has amenable anatomy for the timely placement of 14G or 16G peripheral IVs. Further research comparing the rapid infuser and the infusion times of blood products is warranted.
-

Osteopathic Representation in Orthopedic Literature: A 25-Year Analysis of Publication Trends of Former AOA Residency Programs and Osteopathic Medical Schools
Troy Puga, Ibraheem Qureshi, Hans Drawbert, Michael Muncy, and John T. Riehl
Background Orthopedic surgery remains one of the most competitive specialties. Osteopathic candidates have recently matched at lower rates than allopathic students. One disparity that may exist is research, which has become a critical component of candidate applications. This study aimed to examine the representation of osteopathic-affiliated first authors, senior authors, and overall osteopathic-affiliated authors, in the top 25 leading U.S. orthopedic journals published between 2000 and 2024. Methods A retrospective bibliometric review was conducted on articles published from 2000 to 2024 in orthopedic journals. Journals were selected based on their h-index score. Institutional affiliations were used to identify osteopathic authors. Articles with a majority of authors from foreign institutions were excluded. T-tests and chi-squared tests were used to assess continuous and categorical variables. Multivariate regression identified factors influencing osteopathic authorship. Results 958 articles included osteopathic authors. 570 out of 958 articles with osteopathic authors were published after the AOA-ACGME merger. Senior osteopathic authorship significantly increased the osteopathic author makeup of articles, with the average number of osteopathic authors per article increasing from 0.02 to 2.93 (p<0.001). After the merger, articles with at least one osteopathic author increased from 1.5% of all articles to 3.3% of all articles (p<0.001). When looking at only osteopathic articles before and after the merger, there was a significant increase from 1.82 to 2.22 osteopathic authors per article (p<0.001). Senior osteopathic authorship was also found to significantly increase the odds of having a first osteopathic author (OR: 213.34; 95% CI [165.65, 275.64]; p<0.001). The merger has significantly increased the odds of having at least one osteopathic author in an article (OR: 2.02; 95% CI [1.76, 2.31]; p<0.001). Conclusions Osteopathic physicians, students, and institutions remain underrepresented in orthopedic literature. However, the presence of senior osteopathic authors and the AOA-ACGME merger have positively influenced osteopathic authorship. These findings suggest that reducing the divide between osteopathic and allopathic education, along with enhancing osteopathic mentorship, may help address academic disparities in orthopedics.
-

Out of Left Field LV Thrombus: Incidental Finding in Patient Presenting with Abdominal Pain
Chak Lam Yeung, Shivani Gandi, Shakir Al-Ezzi, Nicole Huang, and Adhikari Pragyan
Introduction: Left Ventricular thrombus (LVT) is one of the most feared complications post myocardial infarction due to the high incidence of embolization. LVT typically form after myocardial infarction and the presence of low ejection fraction (EF), both of which contribute to Virchow’s triad for thrombus formation. LVT are less common in the absence of these risk factors or pre-existing cardiovascular disease. This case report explores the incidental discovery of LVT in a patient, without any known cardiovascular disease, who presented for treatment of acute pancreatitis. Case Presentation: 42-year-old male with past medical history of alcohol use disorder and recurrent pancreatitis who presented with acute abdominal pain and elevated pancreatic enzyme levels. Initial management and evaluation was focused on pancreatitis due to patient’s history of multiple hospital visits for treatment of condition. CT Abdomen and Pelvis was obtained and showed a filling defect in the left ventricle. Further evaluation with transthoracic echocardiography showed a 25mm x 13 mm mobile mass as well as severe akinesis of the apical walls. Due to concerns for thrombus, MRI Brain was also obtained, which showed subacute infarct in left occipital lobe. Patient had left heart catheterization performed but there were no findings of obstructive coronary artery disease. He was transferred to a tertiary care center for further evaluation with Cardiac MRI. Patient was discharged on Eliquis with instructions to follow up with cardiology outpatient. Patient returned to original facility four weeks later for abdominal pain. On second admission, patient reported non-compliance with Eliquis due to cost and lifestyle choices. Repeat MRI Brain revealed new small infarcts. Learning Point: LVT is a rare finding in the absence of cardiac risk factors such as MI or low EF. Patients with alcohol use history are at risk of developing dilated cardiomyopathy and hypokinesis of the apical wall, which can increase the risk of LVT development
-

Perceived Risk of Skin Cancer: Influence of Family History, Age, Ethnicity, and Fitzpatrick Type
Henry Lim, Reem Ayoub, Rafael do Valle, Kristina Kafle, Dana Olsen, Ysabelle Martinez, Christina Guo, Marshall Hall, Christian Scheufele, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Background: Skin cancer in the United States accounts for approximately 50% of new early cancer diagnoses. Despite this, many individuals underestimate their personal risk, leading to lower engagement in preventative behaviors. Several factors may influence an individual’s perceived risk, including family history, age, race, ethnicity, skin type, and gender. While some individuals recognize their increased susceptibility based on personal, familial, and cultural experiences, others may have a lower perceived risk due to misconceptions or limited awareness. This study examines how these demographic factors influence individuals' perceived risk of skin cancer. Methods: This study analyzed data from 333 individuals aged 19 to 92. A questionnaire was conducted reporting age, ethnicity, Family History and two subjective classification methods: self-reported skin color descriptors (very fair, fair, olive, light brown, dark brown, and very dark) and self-assessed Fitzpatrick skin type (I-VI). Participants were sorted into generational cohorts based on their age in 2025: Traditionalists (>80 years), Baby Boomers (61-80 years), Generation X (45-60 years), Millennials (29-44 years), and Generation Z (18-28 years). Statistical analysis used a Chi-square test to examine the association between age groups and sun protection behaviors. Results: Chi-squared analysis found that a family history of skin cancer was significantly associated with a higher perceived risk (p < 2.2e-16). Generation cohort was associated with perceived risk. Older generations perceived a higher risk than younger generations (p < 0.001). Fitzpatrick skin type VI showed a significantly different risk perception compared to other skin types (p = 1.355e-09), while no significant differences were found among skin type I-V (p = 0.546). Gender was not significantly associated with perceived risk (p = 0.25). Ethnicity showed a strong association with perceived risk (p < 0.001). Conclusion: These findings highlight the significant influence that family history, age, and ethnicity have on individuals' perceived risk of skin cancer. The strong association between family history and age with risk perception suggests that personal or seen experiences with skin cancer may play a key role in shaping awareness. The lack of significant association between Fitzpatrick skin types and perceived skin cancer risk suggests that the scale is inadequate for assessing individual risk perception. Our study confirms previous studies that have identified the Fitzpatrick scale's weakness in correctly capturing skin color and ethnic diversity that influences risk perception and awareness. Our study confirms the need for redesigning skin cancer risk reduction programs to increase engagement in preventative behaviors.
-

Postpartum Glucose Testing and Primary Care Follow-up for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Quality Improvement Project
Madeline Bartram, Anusha Hussain, and Timothy Kremer
BACKGROUND: Patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) have a 40-70% lifetime risk for developing type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is 9 times the risk of patients without a history of GDM. Joint association guidelines recommend a 75-gram, 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (GTT) at 4 to 12 weeks postpartum for all patients with GDM, and to follow-up with a primary care physician. Currently, less than half of these patients do not receive the recommended postpartum glucose testing and/or follow-up. METHODS: For each GDM-affected pregnancy, two primary outcome measures were retrospectively collected from the clinic EHR: completion of the 75-gram GTT at 4-12 weeks postpartum and referral to a PCP. The respective variables were marked as completed or not completed and data was allocated to the month in which the patient delivered. RESULTS: From July 2022 to February 2024, 11.8 % (n=46) of the clinic’s patients (N=391) were diagnosed with GDM using the two-step regimen and followed postpartum to collect outcome measure data. Cumulative postpartum compliance rates for patients with GDM were 28% for completion of the 75-gram GTT and 11% for receipt of referral to PCP. Monthly compliance rates varied largely. CONCLUSION: Low postpartum follow-up compliance rates highlight the proposed quality gap for patients whose pregnancies were affected by GDM. Future research should identify specific compliance barriers and investigate their impact upon postpartum follow-up, and ultimately improve compliance rates with deliberate and incremental positive change(s) to the current framework for postpartum and longitudinal care of patients with GDM.
-
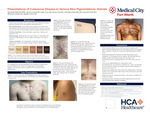
Presentations of Cutaneous Disease in Various Skin Pigmentations: Keloids
Marshall Hall, Alyssa Forsyth, Paige Loux, Henry Lim, Christian Scheufele, Garrett Furth, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Introduction: Keloids are benign, firm nodules resulting from excessive scar formation, typically following trauma, but they can also arise spontaneously. They commonly affect areas like the chest, shoulders, back, cheeks, and earlobes. Their growth exceeds the boundaries of the original injury. Keloids can cause discomfort, pruritus, or cosmetic concerns. While they are more prevalent in individuals with darker skin tones, they occur across all age groups and skin types. Differentiating keloids from conditions such as hypertrophic scars, dermatofibromas, acrochordons, inflamed nevi, cysts, and lipomas i s crucial for proper diagnosis and management. This review highlights the diverse clinical presentations of keloids across various Fitzpatrick skin types. Case Presentation: We present a series of cases demonstrating the diverse presentations of keloids across various Fitzpatrick skin types. The first case involves a 16-year-old male with Fitzpatrick skin type I, presenting with pink, shiny, raised keloids on the shoulders, back, and chest secondary to cystic acne. The second case shows a woman with Fitzpatrick II skin type, presenting with a biopsy-confirmed keloid, described as a firm, pink, linear, well-demarcated raised plaque without adnexal structures, resulting from a previous surgery. The third case features a 17-year-old male with Fitzpatrick III skin type, displaying shiny, pink-to-purple keloids and active cystic acne scars on his chest, shoulders, and back. The fourth case is a 64-year-old female with Fitzpatrick IV skin type, presenting with smooth, linear keloids on her chest resulting from bypass surgery. The fifth case involves a 55-year-old female with Fitzpatrick V skin type, exhibiting linear keloids on her back and smaller plaques on her arm, all darker than her baseline skin tone. The final case is a 73-year-old male with Fitzpatrick VI skin type, who developed spontaneous, hyperpigmented linear keloids across his shoulders, arms, and back. Learning Points: Keloids present differently across Fitzpatrick skin types, often appearing pink or reddish in lighter tones and hyperpigmented in darker tones, highlighting the importance of recognizing these variations for accurate diagnosis. Despite these differences, keloids share common features, including smooth, firm nodules that extend beyond the initial trauma and lack adnexal structures, which help differentiate them from other common conditions such as hypertrophic scars, dermatofibromas, acrochordons, inflamed nevi, cysts, and lipomas. Effective diagnosis and management depend on understanding these variations and employing targeted interventions such as intralesional steroids or surgical excision.
-

Prophylactic Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion in the Management of Placenta Percreta: A Case Report
Monica Rodriguez, Nicole Tenzel, Rachel Russo, and Robert Cohen
Introduction: Placenta accreta spectrum disorders (PASD) are associated with severe maternal morbidity, including hemorrhage requiring massive transfusion, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, coagulopathy, organ ischemia or failure, and death. The adherent placenta results in continuous mixed arterial and venous bleeding, preventing the uterus from adequately contracting. This can result in a blood loss rate of 600 mL or more per minute, posing a risk of exsanguination in less than five minutes. Few reports exist on the prophylactic use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) to reduce obstetric hemorrhage and its application for prolonged occlusion times exceeding 60 minutes. Using the REBOA catheter to manage PASD can potentially improve hemorrhage-related maternal outcomes by minimizing blood loss, facilitating improved operative field visualization, minimizing transfusion volume needs, and shortening surgery duration. Case: The patient was diagnosed with suspected placenta percreta and scheduled for a cesarean hysterectomy at thirty-four weeks gestation. The case was managed by an interdisciplinary team at an Accreta Center of Excellence. Prior to the delivery, interventional radiology placed the REBOA under fluoroscopic guidance at distal zone 3 of the aorta. Central aortic pressure was monitored through the catheter's pressure transducer and compared with the contralateral femoral and radial arterial lines placed preoperatively. Following the delivery and hysterotomy closure, severe hemorrhage secondary to suspected abruption was found after the patient had complete loss of arterial pressure. Inflation of the pre-positioned catheter was able to redirect blood to vital organs, rapidly achieving ROSC and hemodynamic stability. Intraoperatively, the placenta percreta was found to extend from both uterine sidewalls down the entire length of the lower uterine segment involving the bladder and the left ureter. The cesarean hysterectomy with the placenta left in situ was completed with partial and complete occlusion techniques to provide prolonged occlusion for a total of 166 minutes without complications associated with the REBOA. Conclusion: Prophylactic placement of the REBOA catheter has the potential to significantly improve the management of obstetric hemorrhage. This case highlights the efficacy of prolonged endovascular occlusion, utilizing partial and complete aortic occlusion with core aortic blood pressure monitoring to assess hemodynamic status. In cases of acute trauma, REBOA placement is reactive, addressing immediate hemorrhage. However, proactive approaches to obstetric hemorrhage create a unique opportunity, enabling physicians to mitigate complications more efficiently and potentially save lives.
-
Retroperitoneal Schwannoma: An Abnormal Presentation Mimicking a Pelvic Mass
Isabella Sciacca, Christelle Reeves, Cameron Stokes, and Steven Seligman
Introduction: A schwannoma is an encapsulated nerve sheath tumor originating from differentiated Schwann cells. They are preferentially localized to the head, neck and extremities with a minor occurrence of 1-3% in the retroperitoneal space. Schwannoma symptoms often are asymptomatic due to slow growth but can present with symptoms according to their location. We report a case of a 45-year-old female with a retroperitoneal schwannoma that mimicked an ovarian mass. Case Summary: A 45-year-old female with a ten-year history of a right ovarian cyst presented with lower abdominal pain, early satiety, hematuria, low back pain and constipation. Transabdominal ultrasound showed right ovarian enlargement measuring 8.8 x 6.6 cm, described as heterogenous with loculations. Tumor markers indicated a low risk of malignancy. The patient was taken to the operating room for an exploratory laparotomy that revealed a large, firm posterior pelvic mass palpated in the retroperitoneal space. The cyst wall could not be completely dissected due to proximity to major vessels and nerve roots. The patient was referred to a neighboring academic institution because of the case complexity. She underwent repeat exploratory laparotomy and neuroplasty of the L5, S1 and S2 nerve roots. The L5 nerve root was ultimately sacrificed and the retroperitoneal mass was removed. Final pathology revealed a benign schwannoma. Conclusion: The diagnosis of a retroperitoneal schwannoma is often missed because of its rare occurrence, location, vague symptoms and resemblance to other tumors on varying imaging modalities. Due to low incidence and often delay in diagnosis, current management guidelines are limited and not well documented. Currently, histopathological exam after total surgical resection is the most reliable source for diagnosis. The patient in this case demonstrates the need for improvement in the preoperative evaluation and consideration of non-gynecologic differential diagnoses in the evaluation of a suspected pelvic mass.
-

Retrospective Cross-Sectional Analysis of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Effects on Outcomes of Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures in Diabetics
McKenna W. Box, Troy Puga, Neil Werthmann, Yingxian Liu, and John T. Riehl
Introduction: To determine if the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) in type 2 diabetic mellitus (T2DM) patients affects outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures (FNFs). Methods: A retrospective cross-sectional analysis of a local hospital system database was performed using Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) codes to identify T2DM patients who were at least 18 years of age who underwent hemiarthroplasty (HA) for FNFs and were on a GLP-1RA at the time of injury. A random patient sample of those who underwent HA and were not on a GLP-1RA was used as a control. Sex, age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, and Elixhauser comorbidity index (ECI) were control variables. The primary outcomes were initial hospital length of stay (LOS), surgical site infection (SSI) within 90 and 365 days, and medical complications in 30 days. Secondary outcomes were all-cause readmissions within 90 days, implant complications, revision surgery, and in-hospital mortality or discharge to hospice within 365 days. A sub-analysis was performed on patients taking semaglutide, dulaglutide, or liraglutide to those not on GLP-1RA. Results: 499 patients were identified that met study criteria, GLP-1RA use was not significantly associated with an increased risk of medical complication, re-admission within 30 days, hardware failure within 1 year, the likelihood of revision surgery within 1 year, in-hospital mortality/discharge to hospice within 30 days or 1 year, or LOS when controlling for sex, age, BMI, smoking status, and ECI (p>0.5). ECI was associated with increased risk of medical complication, re-admission within 30 days, in-hospital mortality/discharge to hospice within 30 days or 1 year, and LOS (p<0.001). Sex (p=0.0445) and BMI (p=0.0058) associated with increased LOS. No regression for SSI was conducted due to inadequate number of cases (N=6, 1.2%). Conclusion: The results of this study show that T2DM patients on a GLP-1RA at the time of HA for FNF are not at a statistically significant risk of a poor outcome after surgery; rather, ECI is more closely associated with a poor outcome after surgery.
-

Robotic Transabdominal Preperitoneal Morgagni Hernia Repair
Chris Robert and Furrukh Jabbar
Introduction: Morgagni hernia is a rare type of congenital diaphragmatic hernia, representing about 3% of all cases. It occurs due to a defect in the development of the diaphragm in the Morgagni foramen, also known as the sternocostal triangle. Case presentation: A 63-year-old woman with a past medical history of hypertension, hypothyroidism, Barrett’s esophagitis, and cirrhosis secondary to alcohol intake (Child Pugh A) presented with increasing shortness of breath and spasmodic right sided chest pain. A diagnostic workup with a CT chest revealed herniation of fat and a portion of the colon into the right chest with adjacent atelectasis of the lung. This case was done using a robotic transabdominal preperitoneal approach. The herniated contents were reduced, preserving the integrity of the pericardium and pleura. A preperitoneal flap was created, taking care not to disrupt the peritoneum, and the hernia was repaired primarily first using sutures; this was further reinforced with a Progrip mesh. A drain was then placed at the right upper quadrant. The patient had an uneventful recovery and was discharged on postoperative day 2 of surgery. The drain was removed at the 2-week postoperative follow up. Learning points: Morgagni hernia is a congenital hernia due to an anatomical defect in the sternocostal trigone. Although frequently detected in childhood, delayed presentation is more frequently present in females in the fifth decade, with the most common presenting symptoms being gastrointestinal and respiratory. There is still controversy on the optimal approach for surgery. A robotic preperitoneal approach is advantageous in that it allows for precise sac excision, wide dissection of the preperitoneal space, primary repair and mesh reinforcement. Conclusion: Robotic transabdominal preperitoneal approach for the repair of incarcerated diaphragmatic defects is a safe and valid option.
-

Robotic Whipple Procedure
Chris Robert, Soomal Memon, Umar Butt, and Furrukh Jabbar
Introduction: Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive tumor with surgery being the corner stone of multidisciplinary treatment. Pancreaticoduodenectomy is a technically demanding procedure associated with significant morbidity. Case presentation: 70-year-old man with a past history of hypertension presented with jaundice, dark urine and a total bilirubin of 24. His CT scan showed biliary and pancreatic ducal dilation. An EUS revealed a 2cm pancreatic mass with an intact interface between the mass and splenoportal confluence, the biopsy was suggestive of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. We performed a Robotic Whipple procedure. Robotic Whipple surgery is superior in meticulous dissection of the retro pancreatic tunnel. This patient had an uneventful recovery, his drain amylase was 109 on day 3 and he was discharged on post operative day 6. Patient came in for a post operative visit at 2 weeks when the drain was removed Learning points: The ability to achieve R0 resection is about 60% in open cases. Robotic surgery affords clear advantages in that it has more lymph node yield and affords accurate dissection of difficult anatomic zone which are important in achieving a margin negative resection. Robotic surgery facilitates dissection down to the adventitia of the superior mesenteric vein which are important is achieving a margin free resection. We noted superior visualization of retro pancreatic tunnel to take the pancreatic corpus off the portal vein as well. Several studies show robotic Whipple has lower rates of wound infection, blood loss, lower delayed gastric emptying and lower hospital stay. Conclusion: Robotic approach for Whipple procedure defect is a safe and valid option for the extensive resection and reconstruction
-

Severe Hypercalcemia in a Patient Taking Chronic Shark Fin Supplements
Sumanth Reddy and Bishwas Upadhyay
BACKGROUND/INTRODUCTION: In this study, we discuss a case of an 86 year old Vietnamese female who presents with severe hypercalcemia, 15.0, who presented with progressively worsening physical debility which resulted in the patient being wheelchair bound after being found to be taking chronic calcium supplements. Hypercalcemia is a metabolic abnormality that is known to cause muscle weakness, changes in sensorium, dehydrations, nausea, anorexia, polyuria, constipation, fatigue, and depression. CASE PRESENTATION: Patient is an 85 year old female with significant medical history of osteoarthritis who presented to the emergency department for generalized fatigue for the past 2 weeks. Patient reports that she has been progressively weaker. She had not been able to eat anything since the day prior to admission due to nausea and some coughing. Patient also reported pain and weakness in bilateral lower extremities for the past few months. She reports pain in both knees, worse in the right side. Since the pain onset, she has had progressive difficulty, over a 6 month period, with ambulation that resulted in the patient requiring use with a wheelchair. In the emergency department, blood work was significant for Calcium 15.0, elevated Vitamin D at 148 and suppressed parathyroid hormone. Initial imaging obtained was negative for any acute fractures. Further workup for malignancy was negative. Further history revealed patient had been taking 2000 units of calcium supplement extracted from shark cartilage for at least 6 months, reported by the patient. These supplements were discontinued and the patient was treated with medical management of her hypercalcemia. Her calcium improved with treatment back to normal limits at discharge and patient’s mobility improved over the course of the admission. DISCUSSION/LEARNING POINT: In this patient with severe hypercalcemia, workup was negative for malignancy and identifiable cause of her hypercalcemia was related to extrinsic use of calcium supplements from shark fin extract. This case demonstrated the severity of hypercalcemia that can develop with chronic calcium supplement use. In patient’s with severe hypercalcemia such as this, it is important to consider extrinsic causes of severe hypercalcemia in addition to differentials including malignancy. Patient who are taking supplemental calcium/vitamin D should be aware of the potential side effects of toxicity and severe hypercalcemia such as muscle weakness, changes in sensorium, dehydrations, nausea, anorexia, polyuria, constipation, fatigue, and depression and should prompt medical evaluation
-

Severe Hypokalemic Paralysis Following Rituximab Infusion in a Patient with Type I RTA
Ayham Alsaab, Yousuf Sherwani, Emily Devine, Sarah Faheem, Vikas Gullapalli, and Mohan Sengodan
Rituximab is a CD-20 monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of _. Rituximab is a steroid-sparing agent that can be used to control a variety of diseases. (find sources but I found several possible uses). As with any therapy, there are side effects. One potential side effect of Rituximab that has only been described a few times in the literature is hypokalemia. One such report is a case report from 2020 that describes symptomatic hypokalemia in an 18-year-old female with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after her 6th rituximab infusion, with K dropping from 4.0 prior to infusion to 2.3 at the time of symptoms. Did have prior history of dizziness, hypotension and pre-syncopal symptoms after 2 infusions but these were deemed not relevant clinically. The other is a _ conduct by the Saudi Arabia __ that proposes a possibility of rituximab causing hypokalemia, however, does note that these patient’s were also receiving additional chemotherapy agents that These were all in patients with other causes of hypokalemia such as co-administration with another chemotherapy agent or in a patient with underlying nephropathy? Further research should be done potentially on the need for closer monitoring of these patients post transfusion. The purpose of this case is to educate other on the potential electrolyte abnormalities caused by rituximab as these abnormalities can be life threatening. Here we present a case of severe hypokalemia in a patient with underlying Type 1 RTA.
-

Shortness of Breath in a 39 Year Old: A Rare Case of Heart Failure
Mohammed Rashik, Olufunmilola Adeleye, Jason Thompson, and Tasaduq Mir
Currently, 2.6% of Americans suffer from heart failure. Common causes include coronary artery disease, chronic hypertension, arrhythmia, and myocardial infarction, often managed in clinical and hospital settings. A rare cause, however, is infiltrative cardiomyopathy, affecting just 0.04% of the U.S. population. This condition, often caused by amyloid buildup or sarcoidosis, is challenging to diagnose and typically requires a heart transplant due to its rapid progression. Thorough investigations into heart failure causes are crucial to identify this rare condition. A 39-year-old male with no significant medical history presented to the University of North Texas Health Science Center (UNTHSC) Family Medicine clinic with exertional shortness of breath, starting two weeks earlier. An electrocardiogram revealed a new onset left bundle branch block, and he was promptly sent to Medical City Fort Worth Emergency Department. Further tests indicated concerns for decompensated heart failure, and he was admitted for inpatient care. The patient reported no significant medical history, medications, or lifestyle factors. Vital signs included a blood pressure of 131/94 and a pulse of 102. The physical exam showed jugular venous distention, tachycardia, and abdominal distension. Initial lab tests, including complete blood count, thyroid function, basic metabolic panel, troponin, and lipid profile, were unremarkable. However, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) was elevated at 1300, and chest X-ray showed cardiomegaly and pulmonary vascular congestion. Diagnosed with respiratory failure due to acute heart failure, the patient was started on furosemide. A trans thoracic echocardiogram revealed an ejection fraction of 15-20% with severe left ventricular hypokinesis and mild mitral valve regurgitation. Right heart catheterization showed no significant arterial stenosis. The cardiology and heart failure team who were involved from admission suspected infiltrative cardiomyopathy, started him on prednisone and scheduled a cardiac MRI for a definitive diagnosis. His symptoms improved after diuresis, and he was discharged on day five after placement of a life vest. He has kept all follow-up appointments, and the MRI results are pending. This case highlights the importance of recognizing heart failure symptoms, conducting a thorough workup, and involving specialists early. It is particularly noteworthy due to the patient's lack of significant medical history and the rare nature of infiltrative cardiomyopathy. The case also emphasizes evidence-based treatments and interdisciplinary collaboration to manage complex cases.
-

Skin Color Cannot Be Confined to Six Categories: Comparing the Fitzpatrick Scale and Colorimetric Measures
Henry Lim, Kristina Kafle, Reem Ayoub, Dana Olsen, Ysabelle Martinez, Rafael do Valle, Christina Guo, Marshall Hall, Christian Scheufele, Michael Carletti, and Stephen E. Weis
Purpose The Fitzpatrick Scale (FS), originally developed to dose photochemotherapy in Caucasian skin, has become widely adopted for skin color categorization. It originally included types I-IV, with types V-VI added later for darker skin. The FS was designed for UV radiation reactivity assessment. However, it is increasingly used as a proxy for objective skin color classification, despite being based on a subjective questionnaire. Individual Typology Angle (ITA), a validated colorimetric measurement, presents a potential alternative. Previous studies examining these classification systems have been limited by small sample sizes and uneven distribution across skin tones with subjects predominantly having lighter skin tones. This study aims to explore these limitations by investigating the relationship between ITA measurements and Fitzpatrick Skin Types (FST) on a self-reported skin color survey in a cohort including the full spectrum of skin tones. Methods This study enrolled 440 subjects to evaluate relationships between subjective skin typing systems and objective colorimetric measurements. Participants completed a questionnaire covering self-reported skin color descriptors (very fair to very dark) and self-assessed Fitzpatrick type (I-VI). Objective colorimetric measurements were taken on the left inner arm using a colorimeter to minimize sun exposure influence. Individual Typology Angle (ITA) values were calculated from the measurements following established protocols. Statistical analysis was performed using pairwise comparisons with t-tests and pooled standard deviations to evaluate the relationships between ITA values and both subjective classification systems (p<0.05). Results Analysis showed that ITA angle was not statistically significant at predicting Fitzpatrick skin type (p=0.3528) and showed inconsistent predictability of perceived color descriptions (p=0.615). However, ITA angle demonstrated stronger association with self-described skin color compared to Fitzpatrick type (p<2.2e-16). Conclusion Our results reveal that Individual Typology Angle (ITA) measurements and Fitzpatrick Skin Types (FST) represent distinct and non-equivalent systems for skin categorization. While ITA provided more precise differentiation for self-reported skin color, it showed limitations in capturing full skin tone variation (p<2e-10). FST showed no significant differences between adjacent categories I-III (p=0.35286). These findings suggest current categorization options are insufficient, as shown by the lack of statistical significance between adjacent self-reported categories (Olive vs. Fair, p=0.381; Very Dark vs. Dark Brown, p=0.615). Our study indicates the FS's six choices inadequately represent skin color variation; future research should explore both objective measurements and expanded category ranges for improved clinical applications.
-

Streamlining Bubble Study Requests in Echo Orders: A QI Initiative
Vineeth Lekkala, Sharvani Raguthu, Taher Yusufali, Mahmood Ahmad, and Mohan Sengodan
Introduction: This quality improvement project centers around the implementation of a dedicated mechanism for ordering bubble studies in echocardiograms at Medical City North Hills Hospital. Drawing inspiration from successful implementations observed at Medical City Denton Hospital, the project aims to address existing challenges, standardize practices, and improve overall efficiency in the echocardiogram ordering workflow. Background: The echocardiogram ordering process at Medical City North Hills Hospital currently faces challenges, specifically the absence of a dedicated mechanism for ordering bubble studies. This deficiency introduces the risk of oversights, particularly in cases of syncope and stroke, thereby compromising diagnostic precision. Acknowledging these challenges, a quality improvement project is initiated to optimize the ordering process and enhance patient care outcomes at Medical City North Hills Hospital. Methods: The methodology involves initiating discussions with the ultrasound department at Medical City North Hills Hospital to gather their insights and preferences. This collaborative approach aims to ascertain whether the ultrasound department would prefer an update to the existing order or the implementation of a distinct order specifically for bubble studies. Ensuring active involvement and feedback from the ultrasound department is integral to the success of this initiative. Subsequently, the project will engage in discussions with the IT department to determine the most effective and seamless implementation process. This collaborative effort will ensure that the introduction of a user-friendly checkbox or button within the electronic health record (EHR) system aligns with technological capabilities and enhances overall efficiency. Results: Anticipated outcomes encompass the establishment of standardized practices, improved workflow efficiency, heightened physician awareness, and ultimately, enhanced patient care outcomes at Medical City North Hills Hospital. Metrics for evaluation include comparing ordering rates pre and post implementation, and user satisfaction. Conclusion: In conclusion, this quality improvement project at Medical City North Hills Hospital, guided by successful implementations observed at Medical City Denton Hospital, reflects our commitment to providing high-quality patient care. By enhancing the ordering of bubble studies, we aim to contribute to better outcomes for patients at Medical City North Hills Hospital.
-

Telestration with Augmented Reality in Surgery: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hannan A. Maqsood, Minaam Farooq, Laiba Sarfraz, and Michael Truitt
Objective: Augmented reality (AR) telestration has the potential to completely transform surgical teaching and training. In contrast to traditional telestration and telestration without AR, this systematic review and meta-analysis attempted to thoroughly assess the effect of telestration with AR on a variety of performance metrics, including task completion time, error rates, GOALS task-specific scores, OSATS task-specific scores, and GOALS Global scores. Methods: Six relevant publications were included after a thorough literature search was carried out to March 2024 across relevant databases. To evaluate the impact of telestration with AR on performance indicators, meta-analyses were carried out, and statistical analysis produced pooled effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The I2 statistic was used to assess heterogeneity. Results: The meta-analysis showed that when comparing telestration with AR to traditional approaches and without AR, the meta-analysis showed significant gains across several performance parameters. In particular, there was an improvement of 4.99 points (95% CI 0.90 to 9.08; I2 = 81%) in the task-specific OSATS scores and 1.67 points (95% CI 0.57 to 2.78; I2 = 0%) in the Global OSATS scores. Moreover, there was a 1.67 point (95% CI 0.57 to 2.78; I2 = 0%) rise in GOALS Global scores and 1.04 points (95% CI 0.25 to 1.83; I2 = 0%) in the task-specific GOALS scores. Notably, a mean difference of -10.99 (95% CI -34.07 to 56.05; I2 = 68%) was seen in the job completion time when telestration with AR was used. Error rates, however, showed no discernible decrease (mean difference: -18.92, 95% CI -57.93 to 20.08; I2 = 85%). Heterogeneity was explained in task-specific OSATS scores (p = 0.003) and task completion time (p = 0.02). Conclusion: In conclusion, there is strong evidence from this systematic review and meta-analysis to suggest that telestration with augmented reality can improve surgical training outcomes. The technology has the potential to completely transform surgical education, as seen by the notable gains in task-specific scores for both GOALS and OSATS that have been observed, together with the large reductions in task completion times. To address the observed variation and investigate other factors influencing performance results, such as learning curves and long-term skill retention, more research is necessary.
-

The Effect of High Frequency Low Amplitude (HFLA) Vibration on Blood Flow - Literature Review
Zara Soomro, Patrick Feng, Olufunmilola Adeleye, Yi Lei, Aaishah Vohra, Malinda Hansen, and Michele McCarroll
BACKGROUND: Diabetic foot ulcers are a major source of preventable morbidity in adults with diabetes; however, complications impose an increased burden on patients and healthcare systems. Vibration therapy is a potential new modality for DFU treatment, which may be more accessible to individuals. Literature pertaining to the effect of high-frequency low amplitude (HFLA) vibrotherapy on wound healing needs a literature review to help synthesize and integrate the empirical studies' results. The purpose of this study is to review how vibration physiology relates to skin blood flow which impacts wound healing based on previous studies. METHODS: A selective literature review was conducted to investigate the relationship between HFLA vibration therapy and blood flow, which helps with wound care. The selective review was performed using Cooper’s (1988) Procedure for synthesizing literature through the following process: Problem formation, data collection, data evaluation, analysis and interpretation, and limitations to the study. The contents were reviewed to ensure that the articles met the requirements and accuracy of the search. The research aim was to systematically identify the literature to establish the connection between vibrotherapy and blood flow. The articles were later grouped according to their contribution to the research - mechanism of action, frequency types, future applications, and adverse effects. RESULTS: After reviewing and categorizing the papers into major themes, there were four major trends from which the content emerged. The trends included the following: mechanism of action, correct frequency, applications of vibration therapy and adverse reaction to vibration therapy. Vibration therapy works by stimulating a tonic vibration reflex which causes angiogenesis and granulation tissue formation, which leads to increased skin blood flow, vasodilation and microcirculatory alterations. Vibration frequency is a dependent response of the vascular system to repetitive vibration, i.e. increased vibration frequency leads to augmented skin blood flow. Due to the effects of vibration therapy on enhancing blood flow, it is suggested that vibration therapy could be a leading treatment modality to wounds, diabetic or stage I/II ulcers, muscle recovery, cellulite therapy, and skin aging. CONCLUSION: This literature review revealed that vibrotherapy induces vasodilation, which enhances the microcirculation, and by extension, wound healing. These wound-healing properties can be applied in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, bone fractures, and even cosmetic procedures.
-

The Influence of Senate Bill 8 on Permanent Sterilization in Texas Women: A Retrospective Analysis
Isabella Sciacca, Chrystal Stallworth, Cameron Stokes, Hannah Affleck, Timothy Kremer, and Michele McCarroll
Introduction Of the 6.1 million pregnancies that occurred in the United States in 2011, 45% were unintended. Of those unintended pregnancies, 42% ended in elective abortion. In the United States, the most common contraceptive method used is permanent female sterilization. Senate Bill 8 (SB8), also known as the Texas Heartbeat Act, was put into effect on September 1st, 2021. This act virtually bans all abortions after six weeks gestation. This study is aimed at evaluating the association between the implementation of SB8 and patients who underwent permanent sterilization procedures. Methods Patients who underwent permanent sterilization in Texas within a multi-institute healthcare system from January 2018 through December 2023 were included in the analysis. Independent factors such as race, age, and insurance status were analyzed. Permanent sterilization procedures were categorized utilizing current procedural terminology (CPT) coding . A multiple linear regression analysis was used to evaluate the data set for impact of independent factors on rates of permanent sterilization pre- and post- implementation of SB8. Associations between sterilization rates and date of procedures were analyzed using one-sample proportional T testing. Results A total of 5900 patients met inclusion criteria. Patients ranged from ages 19-52. Of the patients included in the study, 59.1% where Non-Hispanic White (W), 10.9% Non-Hispanic Black (B), 9.3% Hispanic (H), 0.8% American Indian/Alaska Native (N), 1.8% Asian/Pacific Islander (A), and 18.1% Unknown/Other race (U). Sample payer mix included 60.2% Medicaid/Medicare, 33.2% Private Insurance, 3.8% Self Pay, and 2.8% other/unspecified. Utilizing September 01, 2021 as a binomial cutoff, 3505 patients underwent sterilization pre-bill, and 2395 patients in the post-bill grouping. A statistically significant decrease in the number of patients undergoing permanent sterilization procedures was observed following implementation of SB8 (p=<0.0001, 95%CI 39.34-41.86). Additionally, there were no observed associations between age, race, and payer type regarding rates of sterilization (p=0.233, 0.341, 0.460). Conclusion Analyses revealed a statistically significant association between dates of sterilization procedure and rates of sterilizations performed in the state of Texas. Timing of procedure is a statistically significant predictor of sterilization rates, with post-bill patients having a reduced rate of sterilization when compared with pre-bill patients. Therefore, the correlation between sterilization dates and decreased rates indicates underlying contributing factors are present that may not have been assessed in this study and warrant further investigation.
-

The Intersection of Hypophysitis and Central Diabetes Insipidus: A Clinical Case Report
Sanjana Kesireddy, Brina Gonzalez, and Mohan Sengodan
INTRODUCTION: Hypophysitis can cause damage to the posterior pituitary, which in turn impairs the production or release of ADH, leading to the symptoms of central diabetes insipidus. Without enough ADH, the kidneys cannot concentrate urine, resulting in the symptoms of excessive thirst and urination seen in central diabetes insidious. CASE PRESENTATION: 27 year old female presents with excessive thirst, headache, nausea and vomiting. Patient had increased urine output since endoscopic trans sphenoidal resection of pituatary mass. She was started on desmpressin 0.2mg orally three times a day. Based on urine specific gravity and urine output per hour, IV desmopressin was added and titrated to decrease urine output. Patient was able to wean off IV desmopressin and discharged home with a tapering course to desmopressin 0.1 orally twice a day for 7 days to a maintenance dose of Desmopressin 0.1 mg daily indefinitely. Additionally, patient was discharged home with steroid dosing of Hydrocortisone 10mg in the morning and Hydrocortisone 5mg in the evening as a maintenance dose. LEARNING POINTS: It was crucial for the patient to be on steroids to reduce inflammation and treat the hypophysitis. It’s crucial that steroid dosing is tailored to the individual patient and adjusted based on factors like the underlying cause, response to treatment, and side effects. The connection between hypophysitis and central diabetes insipidus is that hypophysitis can directly impair the pituitary’s ability to release ADH, which is crucial for regulating the body's water balance. Serial checks of urine specific gravity is important for adjusting desmopressin dosages to ensure effective treatment and avoid complications. For maintenance dosage in patients with central diabetes insipidus secondary to hypophysitis, desmopressin is adjusted to ensure urine specific gravity remains within a normal range, typically around 1.010 to 1.020.
-

The Major League Baseball Pitch Clock: One Year Position Player Injury Analysis
Troy Puga, Nicholas Scigliano, McKenna Box, and John T. Riehl
Background In 2023, Major League Baseball (MLB) implemented the pitch clock. The effects of the pitch clock on player injury rates is largely unknown, and some, including the major league baseball players association, have suggested that pitchers may be at an increased risk of injury with its implementation. Position players have received little attention in these discussions, even though they may be at the same theorized risk of injuries. The aim of this study is to determine if implementation of the 2023 MLB pitch clock influenced the incidence of injuries in position players. It is hypothesized that implementation of the MLB pitch clock will lead to a rise in injuries due to a reduction of time for the primary biological energy system used by baseball to restore to normal levels. Methods Injury data was collected from the fangraphs.com injury database, the most comprehensive MLB data and statistical database website, for the 2021, 2022, and 2023 MLB seasons. The incidence rate ratio was calculated and used to compare the injury rate for the 2023 season to the 2021 and 2022 seasons for both major anatomical categories and anatomical subcategories. A z-test for proportions was used to determine significance. Results Incidence rate ratio comparison of the 2023 MLB pitch clock season versus the 2021 MLB season showed a decrease in the total incidence of injuries (p < .001), lower extremity injuries (p < .001), and hamstring injuries (p = .032). Incidence rate ratio comparison of the 2023 MLB pitch clock season versus the 2022 MLB season showed a decrease in the total incidence of injuries (p = .010), undisclosed injuries (p < .001), and knee injuries (p = .035). Conclusions Following the implementation of the pitch clock during the 2023 MLB season, the total number of injuries and several lower extremity injury categories decreased. Due to a decrease in the overall time spent on the field in a single game and over a season, it could be hypothesized that the pitch clock decreased the workload for position players, leading to this drop in injuries. Further longitudinal investigation must be done to investigate if this influence of the MLB pitch clock persists overtime.

