
North Texas GME Research Forum 2024
On April 19, 2024, Medical City Arlington hosted the North Texas Division Research Forum with 200+ attendees (in-person & virtual), over 300 authors, 12 oral presentations, 34 in-person poster presentations, and 52 virtual poster presentations celebrating scholarly activity from the North Texas Regional Consortium of Medical City Healthcare, University of North Texas (UNT), and Texas Christian University (TCU). The forum was honored to have Dr. Song Li of Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology and Director of Cardiogenic Shock at Medical City Dallas. He spoke about “Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare”.
Research Category Winners
- 1st - Bradley Gustafson; Nasima Mehraban, Amjad Awan from Medical City Arlington Internal Medicine, Comparing the Positive Predictive Value of At-Home Screening Tests with Chronic Anticoagulant and/or Antiplatelet Therapies
- 2nd - Neil Werthmann; Mason Poffenbarger; John Riehl from Medical City Denton Orthopedic Surgery, Comparison of Three Treatments for Fractures of the Humeral Shaft
- 3rd - Chrystal Stallworth; Abel Moron; Nicole Tenzel; Timothy Kremer; Michele McCarroll from Medical City Arlington OBGYN, Surgical Margin Analysis in Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: An HCA Healthcare Retrospective Study
Quality Improvement Category Winners
- 1st - Ariel Moskowitz; Nicole Tenzel; Joshua Mangels; Lyndsay Millican from Medical City Arlington OBGYN, Implementing a Standardized Screening Algorithm for Iron Deficiency Anemia in Pregnancy
- 2nd - Jennifer Austin; April Miller; Alicia Lay from Medical City Plano General Surgery, Multidisciplinary Simulation-Based Trauma Education for General Surgery Interns
- 3rd - Zachary Shields; Enrique Alvarez-Ventura; Curtis Johnson from Medical City Arlington Emergency Medicine, Impact of Vertical Zone Redesign: One Hospitals Experience
Case Report Category Winners
- 1st - Jennifer Austin; Enrique Alvarez-Ventura; Alicia Lay; Christian Minshall from Medical City Plano General Surgery, Survival After Emergency Clamshell Thoracotomy with Bilateral Atrial Appendage Injuries
- 2nd - Ana Adams; Monica Rodriguez; Robert Cohen from Medical Cuty Arlington OBGYN, Four Cesarean Scar Pregnancies Managed at Accreta Center of Excellence at Medical City Dallas Hospital: A Case Series
- 3rd - Raleigh Payton; David Bassa; Furrukh Jabbar; Hassan Ahmad from Medical City Plano General Surgery, Primary Resection of Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumor with Suspected Lymph Node Metastasis: A Case Report
Overall Research Forum Winner (Most Votes):
- Chrystal Stallworth from Medical City Arlington OBGYN, Surgical Margin Analysis in Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: An HCA Healthcare Retrospective Study
-

2-Methyl-2-Butanol (2M2B) Ingestion Related Toxicity
Elizabeth Diaz, Darshan B. Bhatty, Ngoc Vu, and Sathish Karmegam
2-methyl-2-butanol known as Tert-amyl alcohol (TAA) was previously used in the past for its hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and sedative properties.1 Both ethanol and 2M2B stimulate GABA-A receptors causing similar CNS effects.1 Animal studies have shown that toxicity is greater than 2-pentanol, 3-methyl-1-butanol, and ethanol1. 2M2B is replacing ethanol due to its low cost per dose, high potency, and does not produce a hangover as it is not metabolized to aldehydes.1 This case report describes the clinical course of a patient after intoxication with 2M2B and bringing awareness as it is difficult to confirm diagnosis since there are no specific clinical features and diagnostic labs that aid in diagnosing patient. A 41 year-old female with no significant past medical history was found altered on scene by EMS. Patient had ingested 2M2B prior to EMS arrival, was intubated and brought to the hospital where patient was admitted to the ICU with suspicion of intoxication. On EKG patient was noted to be in sinus rhythm. Levels of acetaminophen, salicylate, ethanol, isopropyl, and alcohol methyl were assessed, however, were normal. Urine drug screen was negative. Labs noted AKI with a creatinine of 1.36 - baseline was unknown. VBG noted metabolic acidosis (7.19/45.8/538/17.5). Lactic acid was normal. Although 2M2B has been known to cause increased osmolar gap and anion gap metabolic acidosis, patient’s labs were negative for these findings. Poison control was consulted; recommended observation and supportive care. She was treated with intravenous normal saline, thiamine 100 mg/day, and folate 1 mg/day. Repeat VBG noted improvement of acidosis (7.31/32.6/170/18.2). Propofol was discontinued to monitor neurological status. Symptoms of intoxication gradually resolved and patient was extubated on day two. Patient was not aware of the risk profile and had ingested 2M2B as a means of increasing sexual drive. Prior to discharge patient was educated regarding the hazards of 2M2B use. Resolution of cognitive status and motor functioning were observed and patient was discharged on the third day of hospital course. Diagnosis of intoxication in our patient was based on information by family members. It is difficult to confirm diagnosis as there are no specific clinical features. Although easily detectable via chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), it can be difficult to diagnose in the hospital setting as routine toxicology screens do not have the ability to detect it. As the use of 2M2B increases, it is imperative that we educate our patients regarding the risk profile.
-
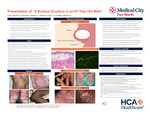
A Bullous Eruption in an 81-Year-Old Male
Garrett S. Furth, Christian J. Scheufele, Carlos S. Bahrami, and Stephen E. Weis
INTRODUCTION: When a patient presents with a blistering rash arriving at the diagnosis can seem overwhelming. Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) is the most common autoimmune blistering disease and tends to affect older individuals, with a mean age of presentation of eighty. It is caused by antibodies targeting the basement membrane zone, the structure between epidermis and dermis, specifically affecting the BP180 (Type-XVII collagen) and BP230 (a plakin) proteins. Antibody-antigen complexes lead to complement activation and destruction of these transmembrane proteins, causing separation of the epidermis and dermis, and formation of tense, subepidermal blisters and bullae. Identification of key clinical features and integrating them with ancillary testing will lead to a diagnosis. CASE PRESENTATION: An 81-year-old male presented with a pruritic, bullous eruption. He had tense blisters and bullae on his trunk, upper, and lower extremities. He also had areas of urticarial or hive-like plaques mixed with ulcerations with overlying serous crust. Unaffected skin did not easily blister with lateral pressure. Evaluation included HSV swab from the floor of a bullae and biopsies for histology and direct immunofluorescence (DIF). Due to the high clinical suspicion for bullous pemphigoid, he was started on systemic corticosteroids after the biopsies were collected. Histopathology and DIF were consistent with bullous pemphigoid. He improved on high-dose corticosteroids. We planned to taper steroids and start treatment with azathioprine. However, during his inpatient stay he was found to have metastatic adenocarcinoma of the gastrointestinal tract and was placed on hospice care. LEARNING POINTS: The differential diagnosis of a bullous eruption is broad and can be initially overwhelming. Blisters and bullae can be caused by many common diseases including herpes zoster, allergic contact dermatitis, insect bites, bullous impetigo, and edema bullae. However, they can also be caused by more uncommon disorders including disseminated herpes simplex, dermatitis herpetiformis, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, pemphigus vulgaris, bullous pemphigoid, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. These conditions can be distinguished through detailed clinical history, physical examination, and ancillary testing. With these data, primary care physicians can better recognize, diagnose, and treat bullous disease, including bullous pemphigoid, in the inpatient and outpatient setting. Early recognition of these disorders may decrease morbidity and lower healthcare-associated costs.
-
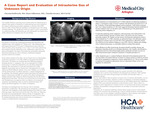
A Case Report and Evaluation of Intrauterine Gas of Unknown Origin
Chrystal Stallworth, Diane Gilbertson, and Timothy Kremer
Introduction: Most reports of intrauterine or endometrial gas have been reported in the setting of underlying gynecologic malignancy or infection. The significance of this case report is to give a presentation of a patient presenting with intrauterine gas who subsequently was found to have neither infectious nor malignant cause for such finding. Case Presentation: Patient is a 56 year old postmenopausal female who presenting with “hip pain” and was found to have incidental intrauterine gas on pelvic CT. She underwent in office and outpatient hysteroscopies with resection of a submucosal fibroid. Her final pathology was returned as benign and ultimately no apparent cause for her intrauterine gas was found. Conclusion: Our case report differs in that our patient was found to have no fistulous abnormalities, was not postpartum nor post procedure, and had no evidence of malignancy on permanent pathology. Our primary goal was to evaluate all potential causes for such finding and provide a differential diagnosis that is not commonly presented in current literature reviews. This case report adds to the literature by providing an alternative presentation for incidental intrauterine air that is not commonly reported.
-
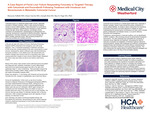
A Case Report of Florid Liver Failure Responding Favorably to Targeted Therapy with Cetuximab and Encorafenib Following Treatment with Irinotecan and Bevacizumab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Maryam Fallahi, Omar Garcia, Joseph Kim, and Ray Page
Introduction: Colorectal cancer, commonly known as colon cancer, is a globally widespread and formidable malignancy originating from the epithelial cells lining the colon and rectum. This disease, demonstrating geographical and demographic variations, particularly prevails in Western countries. The progression of colon cancer typically spans years, initiated by the development of adenomatous polyps, presenting an opportune timeframe for early detection and intervention. The substantial morbidity and mortality rates associated with colon cancer underscore its significance as a public health concern. Various risk factors, such as age, family history, genetic predisposition, inflammatory bowel diseases, and lifestyle factors like diet and physical activity, contribute to its development. A comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis, risk factors, and molecular mechanisms driving colon cancer is crucial for effective prevention, early diagnosis, and the formulation of optimal therapeutic strategies. Case Presentation: A 56-year-old male diagnosed with metastatic moderately to poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma featuring focal signet ring cells in the right colon (pathologic stage IV, colon T3 N2b M1a) presented with a 3.2 cm cecal tumor invading the pericolonic fat, metastatic carcinoma involving 7 out of 12 lymph nodes, and biopsy-confirmed multiple liver metastases. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing revealed a BRAF V600E mutation and KRAS wild type with stable microsatellite instability (MSI). Initial treatment with Irinotecan plus bevacizumab resulted in hospitalization due to florid liver failure. Upon discharge, the patient commenced targeted therapy with Encorafenib and Cetuximab, demonstrating an early clinical response marked by significant improvement in liver function tests and overall performance status. Learning Points: This case report delves into the intricate facets of colon cancer through the lens of a specific clinical scenario involving a 56-year-old male diagnosed with metastatic moderately to poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. The distinctive features of this case, encompassing presentation, staging, and molecular profile, provide valuable insights into the complexities and triumphs encountered in the management of advanced colon cancer. Our examination of this case seeks to contribute to the continually expanding body of knowledge that guides clinical practice, especially with targeted therapy, and elevates outcomes for individuals confronting this formidable malignancy.
-
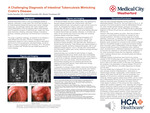
A Challenging Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis Mimicking Crohn's Disease
Justin Sanchez, Gabriel Gonzales, and Monte Troutman
Intestinal tuberculosis (ITB) is an underrecognized disease that shares many clinical, radiologic, endoscopic, and pathologic features with Crohn's disease, making differentiation difficult. This poses a significant problem as initiation of immunosuppressives for an assumed diagnosis of CD in a patient with ITB can lead to exacerbation of infection and life-threatening consequences. A 30-year-old Nepali man with a medical history only significant for Raynaud disease presented with a febrile illness, right lower quadrant abdominal pain, and productive cough over the course of a month. He immigrated from Nepal 3 years prior to presentation, denying other risk factors or specific symptoms of tuberculosis including night sweats or weight loss. Scant rectal bleeding attributed to external hemorrhoids was reported, otherwise, no GI bleed was noted. He had recently been found to have ileitis with worsening symptoms despite conservative therapy. On presentation to our facility, computerized tomography (CT) imaging showed scattered mediastinal, axillary, and right iliac lymphadenopathy, a left upper lobe pulmonary infiltrate, and amorphous nodular densities in the right lower lobe. Abdominal CT showed ileocolic thickening. No additional findings were revealed on subsequent magnetic resonance imaging enterography. His labs were unremarkable and inflammatory markers were normal. Infectious serology and stool studies were negative. Gastroenterology was consulted for ileitis findings on imaging. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) results were unremarkable. Colonoscopy showed two cratered transverse colon ulcers and 20 cm of inflamed, ulcerated terminal ileal mucosa. Biopsies of the colon were benign while the terminal ileum demonstrated caseating and non-caseating granulomas with negative acid-fast bacilli staining. These results were strongly suggestive of Crohn's disease. Tuberculosis testing was performed in preparation for biologic therapy initiation. Mycobacterium tuberculosis polymerase chain reaction and complex testing were negative. However, interferon-gamma release assay was found to be positive. To follow up on this result, a regional lymph node was biopsied and PCR testing of this specimen confirmed tuberculosis. RIPE therapy was promptly initiated. The case presented demonstrates the importance of maintaining a high degree of suspicion for ITB when evaluating cases of suspected CD. Particular efforts to rule out the disease should be made if a high pretest probability exists. This is especially relevant amongst patients from endemic regions. Misdiagnosis risk is increased due to similar presentations between the two disease states and relatively low sensitivity of current ITB testing. Lastly, due to the need for relative immunosuppression in CD treatment, misdiagnosis may directly cause adverse outcomes in ITB.
-
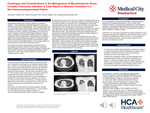
A Common Complaint with an Unexpected Diagnosis: A Case of Mycobacterium avium Complex Pulmonary Abscesses
Maryam Fallahi, Mark Cheneler, Qazi Haider, and Madhukanth Reddy
Introduction: Mycobacterial infections are an atypical organism for pulmonary infections. These infections are classically separated in tuberculous (MTB) and nontuberculous (NTM) groups due to their differing pathogenicity and microbiologic therapy regimens. MTB is typically treated with a 4-drug therapy known as RIPE (rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) however NTM is typically treated with 3- or 4-drug therapy with a backbone of rifampin, macrolide, and ethambutol. Due to the long courses of therapy required for NTM, stringent diagnostic criteria of clinical, radiologic, and microbiologic findings are required. Despite meeting all 3 criteria for diagnosis, not every patient is a candidate for systemic therapy. Treatment courses often extend to 18 to 24 months as 12 months of negative microbiology are necessary to deem a patient as cured. Here we present a case of Mycobacterium avium complex infection of the right lower lobe complicated by abscess formation. Case presentation: A 61-year-old female with past medical history of pneumonia 8 years prior to evaluation but otherwise no prior pulmonary medical history and no history of immunocompromising conditions present for evaluation of acute cough. She was found to have a right lower lobe pneumonia which was further evaluated with computed tomography (CT) of the chest revealing multiple abscesses in the right lower lobe. Evaluation for fungal infections of Aspergillus, Candida, and histoplasmosis were negative. A sputum acid-fast bacilli (AFB) culture would grow MAC sensitive to aminoglycosides and macrolides. She would be started on 4 drug therapy and has continued to follow-up in the infectious disease clinic. Discussion: Optimal patient selection for treatment remains difficult due to the extended length of treatment and potential for toxicity. With treatment lengths extending beyond 18 months, patient adherence must be taken to consideration. Previous studies have shown peak serum concentrations of antimicrobiologic therapy to frequently be below therapeutic range which is exacerbated by rifampin as a cytochrome P450 inducer. Liposomal amikacin for inhalation has shown potential to improve microbiologic conversion rates and has decreased systemic uptake and toxicity; however, cost remains a limiting factor for more widespread use. More studies are needed to develop optimal treatment regimens for patient compliance and microbiologic cure rates.
-

Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19
Tristan Fun, Natalie Hurlock, and Danielle Ford
Introduction: Patient with COVID-19 are more likely to have thrombotic events, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). There have been many case reports of patient with acute mesenteric ischemia (AMI) in the setting of COVID-19. Incidences of AMI occur in about 0.1% of acute hospital admissions. Short term mortality from AMI range from 26-86%. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are essential, yet diagnosis is difficult and AMI can often go unrecognized as a cause of death. This study attempted to establish the risk of patients with COVID-19 having acute mesenteric ischemia and compare it to the risk of patients without COVID-19 having acute mesenteric ischemia. Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study that was done with secondary retrospective analysis of existing, de-identified data. Patients included were those who were hospitalized at a North Texas HCA Healthcare affiliated hospital from March 2020 to October 2021. Patients were included from the database using ICD-10 codes. The main variable looked at in this study was patients with COVID-19 with patients without COVID-19 as the control. The main outcome measured was AMI. Results: The total number of patients obtained from data query was 168,824 from March 2020 to October 2021 (N = 168,824). COVID-19 status was 22,095 (13.09%) positive and 146,729 (86.91%) negative. There was a total of 41 patients with AMI (0.02%). Three patients (0.01%) in the COVID-19 positive cohort had AMI while 38 patients (0.03%) in the COVID-19 negative cohort had AMI (RR 0.5243, 95% CI 0.1619 to 1.6983, p = 0.2816). Conclusion: The results of this study showed that there is no statistically significant increased or decreased risk of AMI in COVID-19 positive patients. There were several limitations in this study. One limitation was a low number of AMI in COVID-19 positive cohort limiting the power of the study. Another limitation could be the underdiagnosis or incorrect coding of AMI. Given that there are some significant limitations to this study, future studies to compare the risk of AMI in COVID-19 patients can be done on a population that more reflects the general population. There will also need to be attention given to the number of patients in each cohort to provide enough power for the study given the expected incidence of AMI.
-
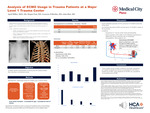
Analysis of ECMO Usage in Trauma Patients at a Major Level 1 Trauma Center
April Miller, Megan Post, Crescens Pellachia, John Bini, and Morgan Collom
INTRODUCTION: ECMO has been used for decades in patients where adequate oxygenation could not be achieved using traditional efforts. Despite its increasing use in the trauma setting, there is a lack of published data to support its use and safety. This review will seek to answer among trauma patients who receive ECMO what their common demographics, injuries, co-morbidities, outcomes and adverse events are. METHODS: This is a single-center retrospective chart review conducted at an Level 1 trauma center between 2020 and 2023. Designation as trauma and ECMO utilization were the inclusion criteria. Patients under age 18 and non-trauma ECMO patients were excluded. Study variables included patient demographics, MOI, number of days on ECMO, hospital LOS, type of ECMO, survival to decannulation, injuries, co-morbidities, survival to discharge, and adverse events on ECMO. RESULTS: All 20 included patients were placed on VV ECMO. 19 males and 1 female were included. The average age was 28.5 (18-70) years. BMI average was 34.3 (19.9-50.7). The mean days on ECMO were 9.1 (2-29) and mean inpatient LOS was 33.85 (3-76) days. 19/20 (95%) of patients survived to decannulation. Survival to discharge was 16/20 (80%). Mechanism of injury included 17/20 (85%) blunt, 2/20 (10%) penetrating, and 1/20 with 40%TBSA burns. Of the 20 patients reviewed, 7 (35%) suffered TBI. Of the patients with TBI, 4/7 (57%) survived to discharge. 3 of the 4 patients who did not survive until discharge had documented TBIs, but overall rate of survival with TBI was (57%). The most common injury noted was rib fractures with a mean of 4.6 (0-13) per patient. 10 patients (50%) had pneumothoraces and 7 (35%) hemothoraces. Blunt cardiac injury affected 4/20 (20%). The most common co-morbidity was hypertension, occurring in 6/20 (30%). 3/20 (15%) of patients had diabetes mellitus. The most common complication during ECMO was bleeding requiring transfusion, which occurred in 9/20 (45%) of patients. 3 patients (15%) developed DVT. Two patients (10%) developed DIC. One patient (5%) had limb ischemia. CONCLUSION: ECMO usage in the trauma setting is an important adjunct in care. This allows additional time for pulmonary recovery and may increase survival and improve overall outcomes. The outcomes from our limited study showed a higher survival rate (80%) compared to the current published outcomes (57%) of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO). Future research with increased sample size will be invaluable for the continued understanding of the role of ECMO in trauma.
-
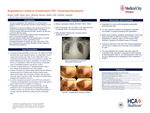
Angioedema Linked to Combination Pill Trandolapril/Verapamil
Aadil Bhutta, Sana Khan, Monica Dhiman, Udit Bhatt, and Akinjide Onifade
Angioedema is the swelling of deeper layers of skin caused by a build-up fluid, oftentimes due to the culmination of immune system activation against allergens. There are several causes of angioedema, including animal dander, exposure to various foods, insect bites, and medications such as Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). This swelling primarily presents periorbital and periorally, however can also less-commonly affect the airway. Angioedema can be life-threatening if involving the throat and larynx given the potential of respiratory airway compromise. This case presents a patient who had been on an ACE-ARB for almost 2 decades, however when switched to the combination drug of Trandolapril/Verapamil, developed life-threatening angioedema. This highlights the rare complications of this combination drug and the need for further research in the more serious adverse reactions of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers versus non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers.
-
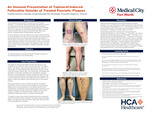
An Unusual Presentation of Tapinarof-Induced Folliculitis
Ysabelle Martinez, Christian J. Scheufele, Christopher Wong, and Stephen E. Weis
Introduction: Tapinarof 1% cream is a novel non-steroidal topical medication recently FDA-approved for plaque psoriasis. Tapinarof’s non-steroidal mechanism allow for longer treatment periods without topical corticosteroid side effects e.g. skin atrophy, hypopigmentation, telangiectasias, and striae. Adverse events identified during pivotal trials may not be completely defined before widespread clinical use. This case reports a new presentation of folliculitis with tapinarof use. Case Presentation: A 25-year-old female with trisomy-21 presented for a rash on her left lower leg. The eruption began one year earlier. The eruption was not associated with pruritus, joint pain or nail changes. A clinical diagnosis of plaque psoriasis was made. Due to unsuccessful response with topical steroids and topical vitamin D analogues, alternative treatment was started with topical tapinarof. After approximately two months of treatment, the patient presented with a new concern of an itchy rash. On exam she had follicular papules around the original plaque. In addition, she had follicular papules and pustules following a linear distribution ascending the affected leg. These papules were distant from the original eruption. There were similar scattered papules on the unaffected leg. A clinical diagnosis of folliculitis was made. Bacterial and fungal cultures were negative. A biopsy demonstrated folliculitis and special stains did not show organisms. Learning Points: Tapinarof cream is a novel non-steroidal treatment option for plaque psoriasis. Tapinarof is considered by many to have a better safety profile when compared to topical steroids. Adverse events reported in tapinarof clinical trials included folliculitis at or near the site of psoriatic plaque. This case is unique as the folliculitis occurred not just at the site of application, but also occurred distant to the site. The distribution has not been previously reported. Our case provides histological confirmation of folliculitis as a side effect. Additionally, our case demonstrates that this adverse event may occur in areas outside of the intended treatment area. This unusual distribution of folliculitis may be due to external factors such as transfer of the medication by bed sheets or clothing. An alternative theory may be scratching of the plaque then subsequent spread to the areas where folliculitis is now evident. Further experience with tapinarof will more completely define tapinarof associated folliculitis. In the meantime, clinicians treating patients with tapinarof who develop folliculitis need to consider this possibility in their differential diagnosis.
-
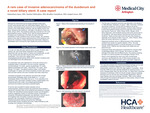
A Rare Case of Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Duodenum and a Bovel Biliary Stent: A Case Report
Sabastiana Sanz, Nasima Mehraban, Bradley Gustafson, and Amjad Awan
Adenocarcinoma of the duodenum is a rare but aggressive malignancy making up less than 0.5% of gastrointestinal cancer cases (Tuan et al., 2023), (Cloyd, 2016). We present a rare case of invasive adenocarcinoma of the first part of the duodenum and major papilla that required complex biliary stenting. A 72-year-old male was admitted to our hospital for further workup of gastrointestinal bleeding and 30-pound weight loss. Through imaging it was noted he had lymphadenopathy and biliary dilation. Patient underwent multiple gastrointestinal procedures and was endoscopically found to have a circumferential mass within the ampulla. After unsuccessful cannulation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, a transmural duodenal-common bile duct stent was placed to improve obstruction. Fine needle aspiration of the mass showed pathology significant for primary duodenal carcinoma for which he underwent chemotherapy. While undergoing chemotherapy, it was noted that patient’s original stent was clogged. Patient subsequently underwent complex ampullary stent exchange procedures including a percutaneous transhepatic-transmural duodenal rendezvous maneuver. This case report will discuss a rare case of invasive adenocarcinoma of the duodenum that required complex biliary stent exchange and novel stenting method. Due to the rarity of duodenal cancers and the complexity of the stenting procedures, our case report will help add to the field to better understand this subject.
-

A Retrospective Study on the Effect of RAAS Pathway Inhibitors at Decreasing the Risk of Acute Coronary Syndrome in Hypertensive Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis as Compared to Other Antihypertensives
Yousuf Sherwani, Asad Risvi, and Senthil Thambidorai
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic multi-system inflammatory disease of which is characterized by articular and extra-articular involvement. Patients with RA have a higher risk of mortality when compared with the general population, which is due predominantly to increased cardiovascular disease. Due to the higher incidence of CVD and MI in RA patients it has been postulated that enhanced systemic inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of CVD in RA patients. Previous studies have shown that ant inflammatory medication such as systemic steroids and immune blockers have been shown to decrease the risk of MI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Our results found that there was a decrease in the risk of ACS In patients taking ace inhibitors however the p value was not sustain due to a lack of sample size.
-

Association of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Treatment with Perioperative and Postoperative Complications in Patients Undergoing Elective Bariatric Surgery
Justin Sanchez, Enith Espinosa, Sean Sojdie, Michael Green, and Lauren Wonderly
Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) are FDA-approved medications for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and obesity, and are also beneficial in cardiovascular risk reduction. However, due to known GLP-1 RA adverse effects, notably delayed gastric emptying, the ASA has implemented GLP-1RA guidelines aiming to minimize potential complications related to GLP-1 RA use in patients undergoing procedures requiring general anesthesia. With the ever-increasing number of patients being prescribed GLP-1 RAs, more research needs to be conducted to investigate their potential impact in other areas of healthcare. This retrospective study aims to compare surgical outcomes before and following the implementation of the ASA guidelines to determine the role of GLP-1RAs in these outcomes. Using data provided by the National Bariatric Data Bank for Medical City Fort Worth, we will compare the outcomes of patients who underwent surgical procedures from 7/1/22-10/31/22 to those from 7/1/23-10/31/23. We will compare the outcomes of each group in regard, to peri- and post-operative outcomes, length of stay, and prior risk factors. We will then determine the number of patients on GLP-1RA therapy in each group and compare the outcomes. We anticipate a significant difference (P<.05) in the number of surgical complications and peri- and post-operative events before implementation of the ASA GLP-1RA guidelines compared to those following. Additionally, we anticipate a significant difference in the peri- and postoperative complications in those patients on GLP-1RAs, whose medication was held before the procedure following the new ASA guidelines. We anticipate a significant difference in peri- and postoperative complications in patients with severe diabetes and disease sequelae, before and following the implementation of the ASA GLP-1 guidelines to hold GLP-1RA therapy prior to procedures requiring general anesthesia.
-

A Unique Case of Spontaneous Pectoral Abscess
Martin Sentmanat, Zachary Shields, and David Ross
Pyomyositis is a rare disease that is often misdiagnosed. Formerly more common in tropic areas, it has been more prevalent in temperate climates in the past couple of decades. Most cases of pyomyositis have a known cause or the patient is immunocompromised, but there are a few documented cases of spontaneous pyomyositis in an otherwise healthy patient. Our case describes a 35-year-old male with no past medical history or history of IV drug use who presented to the emergency department with right sided chest pain. The patient was initially seen and diagnosed with a pectoral muscle strain and fever. He returned several days later with the same symptoms and was ultimately found to have a pectoralis major abscess accompanied by elevated inflammatory and cardiac biomarkers. A subsequent IR drainage of the fluid collection revealed gram-positive cocci in pairs concerning for streptococcus species. There are several case reports of spontaneous pyomyositis in otherwise healthy patients. Some cases with group A strep presume a hematogenous spread from strep pharyngitis. Other reports posit small abrasions as a possible source of pyomyositis from normal skin flora such as staph aureus or epidermidis. However, there is no other documented case in the literature of spontaneous pyomyositis of any location in an immunocompetent adult with an elevated troponin. Given that the troponin elevation resolved after drainage of the pyomyositis, this points to a likely demand ischemia rather than a separate cardiac etiology. Our case reveals that pyomyositis can mask itself as an injury of cardiac etiology, especially given the location of the patient’s pain, such as myocarditis or pericarditis in addition to the usual misdiagnoses of muscle strain or other use injuries. In this way, our case can serve as an example for future clinicians to look for a zebra during their diagnostic workup for chest pain.
-
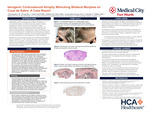
Bilateral Corticosteroid Atrophy Mimicking Morphea en Coup de Sabre: A Case Report
Christopher M. Wong, Jade Pool, Rafael do Valle, Cassandra Kenny, and Dustin V. Wilkes
Introduction: Corticosteroids affect numerous downstream cytokines to exert anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Intralesional corticosteroid injection provides several advantages, including bypassing the stratum corneum to deliver a higher concentration of drug locally, while reducing systemic exposure. Intralesional corticosteroids are used in a variety of dermatologic conditions, and suboccipital steroid injection has been described as a novel treatment for cluster headaches. Case Presentation: A 52-year-old Caucasian female presented to the outpatient dermatologic clinic with indented skin lesions on the scalp and forehead for six weeks. The indentation started on her left frontal scalp and spread down gradually to her forehead and temple. She later noticed the same indentation appearing on her right side. She reported severe pain and the “worst headache” before the lesions started, but there was no further pain after the lesions appeared. Dermatologic examination demonstrated two symmetric hypopigmented linear atrophic plaques extending from the lateral forehead to the frontoparietal scalp on each side. A punch biopsy from the left superior central forehead showed epidermal atrophy with compact orthokeratosis, and scattered telangiectasias within the papillary dermis. Elastin van Gieson staining demonstrated a loss of elastic fibers in the papillary dermis. There was no dermal sclerosis. The adnexal structures, CD34 expression, and the elastic component of the reticular dermis were intact. Direct immunofluorescence studies were negative. Upon further questioning, the patient revealed that she had injections with an unknown medication to the occipital and frontal scalps due to severe headaches from a motor vehicle accident. A diagnosis of steroid-induced skin atrophy was made from clinicopathologic correlation. Learning Points: The adverse effects related to intralesional corticosteroid injections include hypopigmentation, telangiectasias, striae, and atrophy of the skin and subcutaneous fat. When present on the frontal and temporal scalp, atrophic plaques can mimic morphea en coup de sabre, a form of linear localized scleroderma with an autoimmune etiology. Several cases of bilateral morphea en coup de sabre have been previously reported. This case study highlights the importance of obtaining a comprehensive patient history in formation of a differential diagnosis. It also showcases the potential complications of intralesional corticosteroid injections, emphasizing the informed consent process for patients to fully understand possible adverse effects from treatment.
-

Bilateral Spontaneous Osteonecrosis of the Knee (SPONK) in Young Male: A Case Report
Hans Drawbert, Mason Poffenbarger, and Joshua Payne
Introduction: Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SPONK) is a relatively uncommon disease consisting of a focal, subchondral lesion thought to be a subchondral insufficiency fracture that has progressed to collapse and may lead to end-stage osteoarthritis of the knee. There are several treatment options, including nonsurgical and surgical measures but almost 80% of cases end up requiring surgery, usually consisting of unicompartmental or total knee arthroplasty. However, despite these treatment options, there remains no good option for young patients who present with SPONK in large areas of their distal femur or disease in both medial and lateral condyles. Case description: A 25 year old male presented after referral with MRI demonstrating SPONK in both knees. The Left knee involved both medial and lateral femoral condyles and the right knee involved lateral condyle with widespread, severe disease in both. The patient was hardly able to ambulate and had constant pain, making it impossible for him to do daily activities or hobbies without severe pain. After negative medical workup, the patient underwent osteochondral allograft transplantations for his SPONK bilaterally in a staged fashion. With both knees, the patient was pain free at 3 months and is now back to daily life and playing recreational sports with no pain almost 2 years after surgery. Discussion: This case report demonstrates a unique instance of a young, healthy male who developed spontaneous osteonecrosis of bilateral knees with involvement of both medial and lateral condyles of one knee. Our patient was successfully treated with osteochondral allograft transplantation bilaterally, demonstrating that patients in this demographic have another surgical treatment available to them that does not limit their options in the long term.
-

Case Report: Streptococcus Gallolyticus Prosthetic Joint Infection
Jeffrey Dickerson, Liza Salloum, Amaan Sheikh, Madhukanth Reddy, and Bryan Youree
Streptococcus gallolyticus, part of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex (SBSEC) formerly known as Group D streptococi, is strongly associated with colorectal cancer and infective endocarditis. Its appearance in septic arthritis is rare, and its role in septic arthritis has not been as thoroughly investigated. We present the case of a 69 year old male with a history of atrial fibrillation and hypertension who was admitted to our hospital after undergoing a right knee replacement in 2023 with a chief complaint of right knee pain, fever, and chills. Arthrocentesis and blood cultures were performed, and the patient was started on broad spectrum antibiotic therapy with vancomycin and cefepime for empiric therapy of septic arthritis. Patient’s arthrocentesis and blood cultures performed on admission grew Streptococcus gallolyticus sensitive to penicillin and ceftriaxone. On hospital day 3, patient’s antibiotic therapy was deescalated to ceftriaxone monotherapy due to a reported allergy to penicillin. Despite the association of this pathogen with infectious endocarditis, transesophageal echocardiogram performed on hospital day 3 and transthoracic echocardiogram performed on hospital day 5 were both negative for findings of valvular vegetation. Orthopedic surgery team was consulted, and the patient was recommended to transfer to a facility capable of alpha-defensin testing for assistance in diagnosing possible total joint infection. The patient was transferred to an outside facility capable of alpha-defensin testing, and he underwent multiple surgical interventions of the affected joint with full resolution of his infection. Transfer of records from this facility are still pending, but per conversation with the patient, he reports he is doing well since being discharged from this facility. Patient underwent colonoscopy at our facility which was negative for colorectal cancer, but significant for a villous polyp for which the patient will follow up for repeat colonoscopy in 3 years for surveillance. Although a rare finding in the case of septic arthritis, an infection with culture-confirmed Streptococcus gallolyticus is a one that nevertheless warrants swift and thorough workup due to its well-known comorbidity with colorectal cancer and infective endocarditis.
-
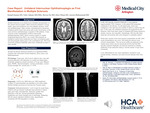
Case Report: Unilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia as First Manifestation in Multiple Sclerosis
Imaad Zaman, Tyler Adame, Steven Do, Kien Nham, and Azeem Muhammad
Multiple Sclerosis is an inflammatory disorder of the central nervous system secondary to myelin degeneration. The disease is mediated by reactive lymphocytes where the spinal cord, brain and optic nerves are attacked. Diagnosis of MS is made clinically and confirmed via MRI with T2 hyperintensities. On presentation, a 26-year-old female with no significant past medical history presented with frequent headaches and blurry vision. There was right eye nystagmus on L lateral gaze with CN III deficits with absent medial rotation. MRI Head presented with a classic presentation of T2 hyperintensities in the subcortical and deep white matter. Further confirmed with NPO Igg antibodies. She was given a 3-day course of high dose Methylprednisolone with moderate symptom recovery.
-

Colon Cancer Symptom Progression in a Non-Adherent Patient: A Case Report
Nasima Mehraban, Bradley Gustafson, Saad Hussain, and Amjad Awan
BACKGROUND: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer mortality and third leading cause of incidence worldwide; accounting for one in ten cancer cases and deaths. Thirty-three percent of people between the age of 50 and 75 are not up to date on screening for colon cancer. Depending on the stage of CRC at the time of presentation, the range of chief complaints that bring patients to seek care for this single etiology is diverse, therefore, a thorough work-up is essential for diagnosis. CASE PRESENTATION: A 55-year-old patient presents to the hospital three times over the course of 18 months, each time with a different chief complaint. The patient is worked-up and the etiology of his complaints is found to be CRC each time. His acute complaints are addressed at each hospital visit and he is given instructions to follow-up in the outpatient setting for further treatment. The patient is non-compliant in the outpatient setting. Thus, with each new hospital visit, the cancer has progressed further, with multiple organ systems becoming involved and demonstrating the diversity of chief complaints which can occur throughout the course of uninterrupted or under-treated colon cancer. LESSONS LEARNED: While the detection of CRC falls under the purview of gastroenterologists through regular screening options, it may also be detected through the involvement of adjacent and metastatically involved organ systems. A thorough history, physical exam, and work-up should be performed by all clinicians to aid in the early detection of CRC in order to improve time-to-diagnosis and outcomes.
-
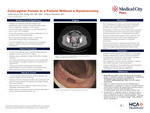
Colovaginal Fistula in a Patient Without a Hysterectomy
Austin Moore, Mollie Ahn, and Anthony Macaluso
Introduction: A majority of case reports and review studies exploring the incidence of colovaginal fistulas typically involve patients of older age with a history of both a hysterectomy and at least one episode of symptomatic diverticular disease. Colovaginal fistulas rarely occur in patients who have not had a prior hysterectomy. Case Description: A 52 year old female presented to colorectal surgery clinic with a history of multiple episodes of sigmoid diverticulitis who now had passage of air and stool from her vagina. She was confirmed to have evidence of a colovaginal fistula from her sigmoid colon to her vaginal fornix on CT imaging. She subsequently underwent robotic assisted lower anterior resection of the sigmoid colon with coloanal anastomosis and repair of the vaginal fornix. She was discharged the following day and had an uneventful postoperative course by the time she followed up in clinic 3 weeks later. Learning Points: This was a rare case of a colovaginal fistula that presented in a patient that had not had a hysterectomy. Prior hysterectomy allows for patients with incidences of diverticulitis to be more prone to having these fistulas due to native tissue derangements and proximity of the vaginal cuff to the sigmoid colon. Even though this patient had an intact uterus, they were likely placed at increased risk for fistula formation given they had a history of multiple diverticulitis flares. Clinicians and surgeons should consider the possibility of a colovaginal fistula formation in patients with a history of diverticulitis presenting with unexplained vaginal discharge or stool passage, regardless of gynecological surgery history.
-

Comparing Large Language Models Accuracy in Following Interval Surveillance Colonoscopy Guidelines
Olufemi Osikoya and Gregory Brennan
Introduction: Providing pathology results and appropriate recommendations after resection of colon polyps is mandatory. Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Google Bard, have shown promise in clinical workflows such as pathology results letters. We tested whether LLMs could provide appropriate surveillance recommendations based on current guidelines from the US multi-society task force for post-colonoscopy follow-up. Methods: Our aim was to compare the accuracy of ChatGPT 3.5, ChatGPT 4, and Google Bard in providing appropriate interval surveillance recommendations. An example prompt being “Write a patient pathology result letter after a colonoscopy with one tubular adenoma polyp (< 10mm) resected. Include recommendations for when the next surveillance colonoscopy should be completed.” Seventeen different post polypectomy surveillance queries and responses were analyzed (correct, partially correct, incorrect) compared to USMSTF guidelines. Results: When comparing the LLMs, Goggle Bard performed the best (TABLE 1). Google Bard provided the most correct responses and the least incorrect responses. Bard provided correct recommendations in 76% of queries (13/17), partially correct recommendations in 18% of queries (3/17) and incorrect recommendations in 6% of queries (1/17). ChatGPT 4 performed better than ChatGPT 3.5. ChatGPT 4 provided correct recommendations in 70% of queries (12/17), partially correct recommendations in 24% of queries (4/17) and incorrect recommendations in 6% of queries (1/17). ChatGPT 3.5 provided the most incorrect recommendations at 24% (4/17). Finally, all LLMs generated readable appropriate pathology results letters with complete information and recommendations. Bard letters were shorter than ChatGPT letters. Conclusion: The LLMs analyzed here provided different recommendations to the 17 post polypectomy surveillance scenarios. Google Bard provided the most correct recommendations. These differences can be explained by Google Bards connectivity to the internet, which ChatGPT lacks. ChatGPT 4 is an updated version and was superior to 3.5. Interestingly, Bard and ChatGPT directly referenced the USMSTF guidelines. ChatGPT 3.5 did not reference any sources. ChatGPT 4 also occasionally referenced the British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE). Overall, partially correct recommendations were common in all LLMs. Using LLMs shows promise but, their current accuracy limits real world adoption.
-

Comparing the PPV of At-Home Screening Tests with chronic anticoagulant and/or antiplatelet therapies
Bradley Gustafson, Nasima Mehraban, Amjad Awan, and Michele McCarroll
BACKGROUND: With the rising incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer (CRC), early diagnosis and treatment is imperative. At-home CRC screening kits are a non-invasive Federal Drug Association (FDA) approved designed to detects either hemoglobin or DNA markers associated for CRC and high-grade polyps. Therefore, therapies that have a propensity to increase rates of gastrointestinal bleeding could theoretically lead to higher false positive rates. The goal of this study was to determine the positive predictive value of at-home screening tests when applied to patients on therapies such as antiplatelet, anticoagulant, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID), or a combination of the three. METHODS: The health system’s enterprise data warehouse was used to retrospectively review patients (>18 years old) who had a colonoscopy and documented in medical notes or lab results as a positive or abnormal at-home CRC screening test. Patients were categorized into five groups: anticoagulant only use, NSAID only use, antiplatelet only use, any combination of the three, or no use of any. Fisher’s Exact Test evaluated the association in rates of diagnosis of colorectal cancer among groups with the different medication use. RESULTS: A total of 1,366 patients were included in this study. Of the 1,366 patients, 62 (4.5%) had anticoagulant only, 114 (8.3%) NSAIDs only, 275 (20.1%) antiplatelet only, 82 (6.0%) combination, and 833 (61.0%) no medications. The results of the study indicated that there was no statistical significance between medication type and rate of positive diagnosis of CRC (p=0.8184). Pairwise comparison tests also did not reveal significant differences of positive diagnosis of CRC between patients using anticoagulant (p=1.0000), NSAIDs (p=0.4683), antiplatelet (p=0.5851), or combination (p=1.0000). CONCLUSION: While no statistical significance was found between pharmacologic therapy groups and rates of positive diagnosis of CRC, the results of this study suggest that these medications do not need to be discontinued prior to conducting an at-home screening test. Further research is necessary to continue to evaluate the impact of polypharmacy combinations and predictive results on non-invasive CRC screening.
-

Comparison of 3 Treatments for Fractures of the Humeral Shaft
Neil Werthmann, Mason Poffenbarger, and John Riehl
INTRODUCTION: Over the past 40 years, surgical treatment for humeral shaft fractures has become more common. The purpose of the study was to evaluate complication rates seen with different treatments for humeral shaft fractures. Nerve injury (NI), infection, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and nonunion (NU) were the specific complications investigated. METHODS: A retrospective database review was performed looking at all patients with humeral shaft fractures. Data was analyzed for complication rates for non-surgical (NS) treatment, open reduction internal fixation (ORIF), and intramedullary nailing (IMN). Inclusion criteria were: 1) patients ages of 18 to 89 and 2) those with humeral shaft fractures. Exclusion criteria were 1) incomplete or incorrect database entry for data points used in the regression analysis, patients with 2) diagnosis of cancer, 3) coagulation disorder, 4) DVT or nerve injury prior to admission/treatment, and 5) pregnancy at the time of fracture. Records were reviewed for presence or absence of complications including infection, DVT, NI, or NU within 2 years of injury. RESULTS: 3,892 patients met study criteria. Patients were more likely to be female (59.48%). 5/531 (0.94%) in the NS group had NI after closed treatment. Patients undergoing IMN developed NI in 3/597 (0.5%), while 47/2,764 (1.7%) developed a NI after undergoing ORIF (p=0.0488). DVT was a rare complication, with a rate of 0.75%. There was no significant difference in the DVT rate among the three groups. NU occurred at a rate of 2%, and did not differ significantly between the three groups. Infection occurred at a rate of 2.39%. The NS group infection rate was 1.13% (6/531). IMN group developed infection in 5/597 (0.84%). ORIF group experienced infection in 82/2,764 (2.97%), (p=0.0010). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: NS treatment, ORIF, and IMN demonstrate similar rates of DVT and NU. ORIF had a higher rate of NI and infection compared to other treatment groups.
-
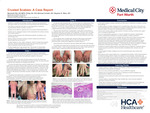
Crusted Scabies: A Case Report
Marshall Hall, Philip Oh, Michael Carletti, and Stephen E. Weis
Introduction: Scabies is a parasitic dermatologic condition that often presents as an extremely pruritic rash. A rare and highly contagious variant of scabies is crusted scabies, formerly known as Norwegian scabies. Crusted scabies presents with hyperkeratotic papules and plaques, most commonly on the palms and soles. Due to the variety of presentations seen in scabies, it can be difficult to diagnose. Case presentation: Case 1: An 89-year-old male with a history of dementia, anxiety, and benign prostatic hyperplasia presented with a 2-month history of a generalized pruritic rash. He lived in a memory care center. The physical exam showed an erythrodermic, cachectic, and diaphoretic patient with scattered erythematous papules, with white hyperkeratotic scale on the trunk. Microscopic examination of skin scaping showed scabies mites, ova, and scybala confirming the diagnosis of crusted scabies. Case 2: A 22-year-old male with a history of trisomy 21 presented with a 10-month history of a mildly pruritic, thick, scaly rash on his bilateral hands and a generalized non-pruritic rash on his trunk, arms, and legs. They report they had seen multiple physicians prior who had prescribed him many medications including topical antifungals. On physical exam, there were thick, hyperkeratotic, white-yellow scaly plaques on the bilateral hands with onycholysis of the fingernails. On the trunk, arms, and legs were pinpoint papules with overlying hemorrhagic crust. Microscopic examination of skin scrapings showed multiple ova and scybala. A punch and shave biopsy of the hands was performed which showed multiple scabies mites in the stratum corneum. Learning points: Crusted scabies is a highly contagious and rare variant of scabies. It is often seen in those who are immunosuppressed, have an underlying neurologic disorder, or are immobile. Patients may present with erythroderma which poses a risk for hypothermia, infection, and high-output heart failure. The mortality rate of crusted scabies is as high as 50% secondary to soft tissue infection and sepsis. Due to the high mite burden crusted scabies is much more contagious and can spread to persons without direct contact. Successful treatment of crusted scabies is more difficult than non-crusted scabies. Successful treatment requires longer treatment than treating usual scabies infestations. Additionally, public health treatment of contacts is needed to control outbreaks and prevent re-infection.
-

Current Trends in School Nursing in Musculoskeletal injuries and Concussions
Christoffer Amdahl, Hans Drawbert, Sadra Forati, Joshua Allen, Sana Qureshi, and Afsha Rais
Background: School nurses are on the front lines of assessing, identifying and treating school age children with a number of health complications. Implementing nursing services in schools have previously demonstrated improved medical care costs for students, less productivity loss for parents, and less productivity loss for teachers. As a result, nursing services in schools provide a cost-beneficial investment of public money, and warrant both financial support from policy makers as well as educational support from local healthcare services. Communicable disease, asthma, musculoskeletal injuries, concussions are common conditions seen in school aged children and a fundamental understanding of these issues is key in appropriate care and treatment. Aim Statement: This study will analyze educational sessions for school nurses regarding communicable disease, asthma, musculoskeletal injuries, and concussion management in school age children in order to improve the gap in continued medical education. Methods: Through online learning modules, in person teaching sessions given by resident physicians from Family medicine and Orthopedic surgery, and in person simulations, school nurses were educated on the care of school aged children regarding communicable disease, asthma, musculoskeletal injuries and concussion diagnosis and triage. Sessions took place in two separate academic year sessions. During the Jan 2023 - March 2023 session, over 885 nurses from 18 different school districts within the DFW were involved, 690 of whom completed surveys. During the 2023-2024 academic year, 900 nurses from 36 school districts were involved or registered in these sessions. Results: Ongoing data collection and educational sessions are being performed at this time, with the target completion date of 3/25/24 and 900 anticipated school nurses in DFW. Self-reported data from participating nurses regarding knowledge regarding the knowledge and treatment will be analyzed from pre and post session surveys, and currently 91% of the participants from the 2022-2023 sessions reported that they would make changes to their clinical practice based on the informational sessions. Additionally, information regarding other recommendations for educational opportunities and session content will be synthesized into qualitative categories. Conclusion: By educating nurses on common school age medical problems, we seek to continue to improve both nursing confidence in primary management of these conditions as well as increase the overall participation from the community in these educational sessions.
-

Cyanide Toxicity Induced by Apricot Kernel Consumption: A Case Report
Jatin Sadarangani, Vaishnavi Singh, and Benjamin K. Kingsly
Functional foods are food items that should be consumed as part of a regular diet in order to provide advantages beyond what are typically referred to as traditional nutritional benefits. Furthermore, in order to support the better function claim or the decreased illness risk claim, these positive outcomes must be scientifically proven. Foods with particular health benefits have been referred to as "superfoods" more recently. Superfoods are conceptually defined as foods with high biological value because of their high concentration of bioactive components and high concentration of nutrients, as well as their high bioavailability and bioactivity in the body. As a byproduct of apricot fruit, apricot kernels are high in carbs, vitamins, and proteins. Additionally, it can be utilized to make food ingredients and for therapeutic purposes. Plants containing fruit and vegetables like sorghum, cassava, lima beans, bamboo shoots, apple seeds, and the kernels of Prunus members like almonds and, crucially, apricot kernels are known to contain cyanogenic glycosides. The latter are most likely to result in acute cyanide poisoning and can contain as much as 6% amygdalin. This case study explores the signs, symptoms, diagnostic challenges, and treatment of cyanide poisoning brought on by eating apricot kernels.
-

Development and Validation of a Novel Skin Pigment Scale
Christina Guo, Henry Lim, Christopher Wong, Christian Scheufele, Michael Carletti, Michele L. McCarroll, and Stephen Weis
Background: Precise description of the skin is a pillar of dermatology. For dermatologists, skin pigment is akin to a ‘vital sign’ in that it represents a basic, yet illuminating, piece of information for each patient. The current method used to describe skin color is the Fitzpatrick scale. The Fitzpatrick scale was designed to measure skin burning and the scale is inadequate for precise measurement of skin color in a diverse population. The prevalence of its use perpetuates harmful and outdated structures and contributes to health disparity. For those reasons, there is a critical need for initiatives that evaluate the current system and innovations which pursue equitable practice. Purpose: In our present study, we aim to develop a novel, accurate, reproducible, and equitable skin pigment scale. Our second aim is to evaluate a unique method to take objective measurements with a smartphone camera. Our goal is to create a skin melanin scale that can serve as a new ‘vital sign’ for dermatologists, researchers, and clinicians to describe skin pigmentation. Methods: An 11-point color scale has been developed that is based on a parameter that approximates melanin. This pigment scale will be reproduced on a physical card which can be placed on a participant's inner arm as a direct comparison for the participant's skin . Both the investigator and participant will choose the scale value that they perceive to match the participant’s skin most closely. Next, a color calibration chart will be used to color-correct photos taken of the same area of the participant's skin with a smartphone camera to measure the skin pigment value. Both measurements of skin pigment, those taken with the card and smartphone camera, will be compared measurements of skin pigment taken by a colorimeter, a pigment-measuring device. We will also compare these measurements to participant's Fitzpatrick skin types as well as self-identified race and ethnicity. Results: We anticipate recruiting n=200 subjects beginning March, 2024, collecting data including measures using skin pigment scale and colorimeter, self-reported information, and photos documenting skin pigmentation. The study team will recruit from a diverse group of participants throughout the North Texas region to ensure equity in subject selection. Conclusion: This novel method of measuring and classifying skin pigment could pose as a quick, accessible, and objective tool for practitioners to use in clinical settings.
-

Discharge Implementation Project: Ascertaining if Discharge Implementation Orders Overall Improves Discharge Metrics at a Texas Hospital
Zachary Paras, Omar Nawab, Komthorn Cunvong, Jackson V. Littlejohn, and Sathish Karmegam
There are several factors preventing discharges out of the hospital within 24 hours that ultimately affects metrics for both hospital systems and physicians. These factors include pending labs, imaging, or procedures; pending placement approval at a facility outside of the hospital upon discharge; notification of family and caretakers; secured funding for devices and medicines; and others. In an attempt to mitigate preventable extra days spent in the hospital once a patient is medically ready for discharge, a Texas hospital implemented a discharge order set for providers to utilize that informs all involved parties including case management, PT/OT, social work, nurses, and others that the patient is medically ready to discharge. This plan was implemented with the primary goal of improving metrics for the hospital and providers that are related to discharge and length-of-stay, and was previously piloted at another hospital in Austin, TX with inconclusive data. The goal, as set by the hospital corporation, was to increase discharges out of the hospital at 11:00 AM and 1:00 PM to 20% and 45%, respectively; before the project was implemented the percentage of discharges by 11:00 AM and 1:00 PM were 7% and 29%, respectively. While it was initially planned to collect data on the rate of use of the order set on one floor, the data was unable to be extracted from data across all floors, so the rate of order set implementation remains unknown. Despite implementation of the order set, the hospital failed to see significant changes in discharge metrics compared to before the order set was implemented, and the order set was abandoned. Future studies on similar measures to improve discharge metrics should include robust data collection methods for detailed analysis of results. Additionally, future studies should be done to see what measures from physician-led notification systems are effective in improving discharge metrics.
-
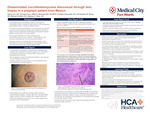
Disseminated coccidioidomycosis discovered through skin biopsy in a pregnant patient from Mexico
Henry Lim, Christina Guo, Marshall Hall, Christian Scheufele, Christopher M. Wong, Michael Carletti, and Stephen Weis
Introduction: Coccidioidomycosis is an infection caused by the organism Coccidioides immitis, a fungus endemic to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central and South America. The presentation of coccidioidomycosis can range from symptoms resembling a simple upper respiratory infection, such as cough, to more severe systemic symptoms including fever, malaise, and chills. Cutaneous lesions of coccidioidomycosis demonstrate a large heterogeneity of clinical manifestations but are significant as they may be the presenting sign of disseminated disease. While usually confined to the lungs, extrapulmonary coccidioidomycosis can occur in about 1 in 200 patients, most commonly associated with immunocompromised status. Pregnancy is an often-overlooked immunocompromised status that is one risk factor for disseminated and severe coccidioidomycosis. A skin biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool when evaluating a skin lesion with undiagnosed infection, especially in the immunocompromised population. Case report: We present a 22-year-old G1P0 female at 34 weeks with no significant past medical history who presented for headache, fever, photophobia, and neck pain for one week. She immigrated to Texas from Chihuahua, Mexico 1 year ago. Despite having prenatal care, a rapidly enlarging verrucous plaque on her forehead was left unevaluated for 2 months. The patient initially presented to obstetric triage 5 days prior to admission due to headache unresponsive to acetaminophen and decreased fetal movement. Labs showed no signs of systemic illness and was discharged. However, due to worsening symptoms, the patient later presented to the ED tachycardic, tachypneic, and febrile with temperature of 102.8F. Kernig’s sign was positive. CT head and chest x-ray were unremarkable. Lumbar puncture was negative for bacterial or viral organisms but revealed eosinophilia. Punch biopsy of the forehead skin demonstrated granulomatous inflammation and scattered foreign body giant cells. Within the granulomatous inflammation were spherules recognizable as coccidioidomycosis. Coccidioidomycosis serology by complement fixation of the remaining CSF fluid was later found positive. The patient was started on amphotericin B but experienced fetal heart decelerations and maternal hypoxia. She was subsequently switched to fluconazole. The patient demonstrated clinical improvement and was transitioned to daily oral fluconazole indefinitely. Several months later the patient delivered a healthy baby without complications. Learning points: A full body skin examination is recommended in patients with an unknown source of infection. Skin biopsies provide valuable diagnostic information in febrile, immunocompromised patients with skin lesions. Pregnancy is an often-overlooked immunocompromised status that has been recognized as a risk factor for disseminated and severe coccidioidomycosis with increasing rates of dissemination by trimester.
-

Early Implementation of CHF Orders and Physician Education
Qazi Haider, Tapannita Padhi, Hunter Thornberg, Barry Brown, Alexandra Villacres, Justin Roy P. Sanchez, and Ashley Henderson
Each year, 700,000 patients are hospitalized with acute decompensated congestive heart failure. In order to effectively treat these patients, they require delicate management of volume status. Measuring volume status incorporates the following components: recording strict inputs and outputs of urine/fluids, recording daily standing weights and fluid restriction. This project focused on recording daily weights as a measure of accurate volume status and how that affected length of hospital stay. Data will be gathered by patient chart review including patient's admitted from Jan 2023 -Jan 2024 at Medical City Weatherford admitted with a primary/admitting diagnosis of congestive heart failure. Using PDSA framework, we will investigate if measurements of daily weights were consistently recorded and if they impacted a patient's length of stay. During course of investigated, it was discovered a potential gap specifically utilization of the order set in measuring daily weights, initially an order needs to be placed for daily weights; second, a daily weight has to be recorded by a patient care tech/nurse. In order to improve a 10% usage of daily weights in 1-month education was provided to residents regarding CHF order set usage upon admission, introduction of printed and digital management index cards, and implementation of "favorite order sets" in Meditech. In conclusion, we noted a shorter length of stay with patients who had consistent daily weights orders in place on admission.
-

Effect of the Intern Survival Book Handbook in Medical City Fort Worth Family Medicine Residency Program
Nancy Sang, Harry Pham, Tammy Nguyen, Zara Soomro, Patrick Feng, and Ali Al-Nahi
Background: The optimization of medical training is a critical concern amid dynamic shifts in both medical and societal landscapes. Research indicates that a substantial proportion of medical trainees experience stress, anxiety, and depression, with an estimated depression rate of 29% among medical residents, compared to 8% among nonphysicians. Furthermore, the suicide rate among physicians is twice that of the general population. Difficulty in adapting to new environments, responsibilities, and training levels exacerbate these challenges. This study evaluates the efficacy of "The Intern Survival Handbook" in mitigating stressors among new trainees, enhancing their work performance, and promoting overall mental health. Methods: Our team developed a comprehensive guidebook, incorporating advice from multiple generations of residents, covering logistical information, daily workflow, and fundamental insights into common pathologies for each rotation during the intern year. A survey, consisting of five Likert Scale items, will be administered to our residency body (excluding members of this study. This will be done as part of a resident wellness survey that was initially sent out during Fall 2023. The plan is to repeat this wellness survey in March 2024, with addition of the five Likert scale questions specific to the MCFW Family Medicine residents. Afterwards, the plan is to use Chi-square analysis to determine if there is a statistically significant difference in wellness. Results: Of those participants completing the survey (n=8), 50% split between agree (n-4) to disagree (n=4) on “I felt prepared to come into residency and handle clinic and hospital responsibilities”; 100% agreed or strongly agreed that “I find that I learn most in rotations where I can perform at my highest level”;
100% agreed or strongly agreed on “I find that reviewing the Intern Survival Handbook before and during rotations has helped me perform to the best of my abilities during that rotation”; n=7 agreed or strongly agreed that “ I find that there is a correlation between my mental health and how I perform in my rotations” versus n=1 strongly disagreed; and
100% agreed or strongly agreed on “I will recommend the Intern Survival Handbook to future generations of residents that come by this program”. Discussion: Amidst the evolving challenges in medical education, we hope our project will reveal that the implementation of a guidebook for incoming trainees within our residency program alleviated a significant mental burden, enabling them to learn and develop to their fullest potential. This approach addresses the multifaceted challenges faced by medical trainees and emphasizes the importance of tailored resources in promoting their well-being and professional growth.
-
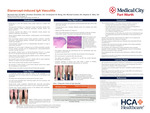
Etanercept-induced IgA Vasculitis
Marshall Hall, Christian Scheufele, Christopher Wong, Michael Carletti, and Stephen E. Weis
Introduction: IgA vasculitis, formerly known as Henoch-Schoenlein purpura, is a subtype of leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV) and approximately 90% are seen in the pediatric population. In the adult population, it is more frequently associated with a more severe clinical course. Causes of IgA vasculitis may be idiopathic or may be secondary to infections or medications. Etanercept is a tumor necrosis factor-alpha fusion protein that has been rarely associated with LCV. Case presentation: A 59-year-old female with a 2-year history of red-to-violaceous purpuric papules on the bilateral lower extremities. She noted that after etanercept administration her lesions would get redder and would become more numerous. She was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis over 20 years ago. She had been treated with methotrexate and etanercept for approximately 5 years. A biopsy of the lesion showed LCV. Direct immunofluorescence showed granular deposition of IgA and C3 within small vessels, consistent with IgA vasculitis. Serum BUN, creatinine, and urine analysis were normal. Learning points: IgA vasculitis is a serious illness that may be associated with systemic organ involvement. It can lead to renal insufficiency and require dialysis. Identifying an underlying etiology may allow treatment that resolves this condition. We identified a patient whose disease was exacerbated by etanercept therapy and is 80% better after stopping etanercept. She had full resolution of any lesions with colchicine within 2 weeks of starting therapy. As biologic therapies become increasingly prevalent, associated adverse events are expected to similarly become more frequent. Recognizing such adverse events is important to prevent the progression of the disease and its associated comorbidities.
-

Four Cesarean Scar Pregnancies Managed at Accreta Center of Excellence at Medical City Dallas Hospital: A Case Series
Ana Adams, Nicole Tenzel, Monica Rodriguez, and Robert Cohen
Cesarean Scar Pregnancy results from pathologic implantation of a gestational sac into a hysterotomy scar. This rare disease continues to increase in incidence due to the rise of Cesarean delivery in the United States. Current management recommendations by the Society of Maternal Fetal Medicine (SMFM) include termination of pregnancy, or in rare instances, hysterectomy. This case series examines four patients diagnosed with Cesarean Scar Pregnancies that either declined termination or were unable to receive abortion services in the first trimester, and who were managed at the Accreta Center of Excellence at Medical City Dallas Hospital. This novel management strategy included admission to the inpatient antepartum service between 30 and 32 weeks gestation, delivery at 34 weeks gestation via planned cesarean hysterectomy with the Accreta team per accreta protocols (or sooner as indicated), and infant NICU admission. All four patients were delivered with viable neonates, received cesarean hysterectomy, and had less than 2500mL of blood loss at delivery. This case series seeks to examine the current recommendations for cesarean scar pregnancies and propose a safe alternative protocol for CSP expectant management within the Accreta centers of excellence.
-
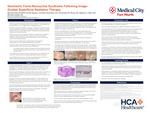
Geometric Favre-Racouchot Syndrome Following Image-Guided Superficial Radiation Therapy
Marshall Hall, Cecilia Nguyen, Christian Scheufele, Christopher M. Wong, Stephen E. Weis, Michael Carletti, and Henry Lim
Introduction: Favre-Racouchot Syndrome is a cutaneous disease characterized by nodules, cysts, and comedones located in sun-exposed areas of the face. It is most commonly found on the bilateral temporal and periorbital skin. Favre-Racouchot Syndrome is most associated with chronic sun exposure. It occurs more commonly in cigarette smokers. It has been rarely associated with radiation therapy. It has not been reported after image-guided superficial radiation therapy or in a geometric pattern. Case presentation: We present the first two recorded cases of Favre-Racouchot Syndrome occurring in the setting of image-guided superficial radiation therapy. Both patients presented with well-demarcated geometric plaques with large open comedones isolated to the treatment field. One patient had a plaque on the forehead and the other on the midface. Both patients were current users of tobacco products during their radiation treatment. Both patients were initially treated with adapalene 0.1% gel nightly to the affected area. Shave removal followed by curettage was performed on the nasal lesion with the resolution of the majority of comedones. Histopathology of the removed lesions showed dilated follicular orifices filled with cornified debris forming comedones. Learning points: The combination of underlying chronic actinic damage, radiation, and tobacco use may increase the risk of developing Favre-Racouchot Syndrome. While patients are undergoing radiation treatments it may be beneficial to abstain from tobacco until treatments have been completed and the skin has healed. This may help to prevent Favre-Racouchot Syndrome in the setting of radiation treatments. Favre-Racouchot Syndrome is easily recognized by its geometric pattern. The differential diagnosis includes skin cancer recurrence. Image-guided superficial radiation therapy is becoming a more common treatment for non-melanoma skin cancers. Patients are concerned these skin changes represent a recurrence of their skin cancer. It is important for clinicians treating persons with non-melanoma skin cancer to be aware of this complication. This will allow patient reassurance and reduce biopsies. Geometric Favre-Racouchot Syndrome can be treated with curettage.
-
Gut Fermentation Syndrome: Unraveling the Enigma of Auto-Brewery Syndrome.
Jatin Sadarangani, Vaishnavi Singh, and Sathish Karmegam
A disorder known as "auto-brewery syndrome" or "gut fermentation syndrome" occurs when bacteria or fungus in the urinary, oral, or gastrointestinal tract ferment endogenously, producing ethanol. Patients with auto-brewery syndrome frequently report eating a diet heavy in sugar and carbohydrates and exhibit many of the symptoms and indicators of alcohol intoxication while disputing alcohol consumption. Research on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease indicates that endogenous alcohol synthesis may have bacterial roots; these bacteria may also be the causative agents in GFS. Probiotics, low-carb diets, anti-fungal medications, and antibiotics are currently used as therapies for GFS. Fecal microbiota transplantation may also have a part in the management of GFS. This case report discusses a case of gut fermentation syndrome complicated with NASH cirrhosis, esophageal varices, and portal hypertension. The case report further investigates the clinical presentation, diagnostic journey, complications, and therapeutic management of a patient diagnosed with auto-brewery syndrome. In this case report, we discuss a 50-year old male who had presented with recurrent anemia concerning for a GI bleed leading to multiple blood transfusions. Management included patient education regarding the condition and discussing lifestyle changes such as a strict adherence to a low carb, high protein diet. The case report further discusses the medico-legal implications commonly associated with gut fermentation syndrome.
-

Horner’s Syndrome, a Rare Complication of Transcarotid Artery Revascularization
Mollie Ahn, April Miller, Shonda Banegas, Edic Stephanian, and Morgan Collom
Extracranial carotid artery aneurysm is a rare sequela of atherosclerosis, trauma, and conditions of chronic inflammation. Standard treatments include antiplatelet medications, open resection, or endovascular stenting. Transcarotid artery revascularization (TCAR) has become a well-recognized alternative treatment in the past few decades. This case study documents the first reported case of Horner’s syndrome post-TCAR for an internal carotid artery (ICA) aneurysm. A 68 year-old male with intermittent double vision was referred to vascular surgery clinic with brain CT angiography showing a 9mm saccular aneurysm with dissection flap of the right cervical ICA. Prior attempts by neuro-interventional radiology were unsuccessful due to tortuous anatomy. After lengthy discussion with the patient, the decision was made to proceed with TCAR. The TCAR procedure was conducted with flow reversal from the right common carotid artery (CCA) to the left femoral vein. A Iliac covered stent, arterial stent was used to stent the lesion. Angiography demonstrated a small dissection at the cavernous segment of the internal carotid artery (ICA). A second stent was placed across the dissection. The completion angiogram showed no residual lesions. Patient was monitored in the ICU postoperatively. A few hours following the procedure, the patient began to complain of a significant frontal headache despite strict blood pressure control. A CT head was completed without any acute findings. Post-op day 1, the patient developed Horner’s syndrome with symptoms of mild right eye ptosis, anisocoria with excessive right eye tearing, and flushing of the face. Post-op day 2, the patient remained stable with persistent Horner’s symptoms. The patient was discharged with tapered methylprednisolone sodium succ regimen with planned close follow up in the clinic. At two-week follow-up, the patient’s symptoms had nearly resolved Horner’s syndrome has been documented as a rare complication following other endovascular carotid procedures. Stretching of the sympathetic fibers that course along the carotid artery is thought to be the cause of this rare complication. Treatment is generally supportive, but there has been documented cases of steroid use. The case highlighted describes a rare and previously undocumented complication of TCAR in high carotid artery lesions. This case will further help understand the possible complications of performing the TCAR procedure and assist in patient selection and treatment discussions for future carotid artery lesions.
-

Identifying Critical Factors in Facilitating the Application of the Team STEPPS Curriculum for Improved Patient Safety in Two Area Skilled Nursing Facilities
Nancy Sang, Jennifer Severance, Sarah Ross, Valerie Agena, and Jane Oderberg
Background: Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs) play a crucial role in long-term care for a progressively frail patient demographic. Surveys of SNF staff reveal poorer levels of safety culture compared to their hospital counterparts. Quality of clinical care delivery in SNF remains inconsistent and insufficient evidence-based process of care. Studies demonstrate that team functioning and communication are crucial in changing the clinical practice methods in SNF. TeamSTEPPS is a curriculum designed to enhance team performance in healthcare settings by addressing patient safety issues and improving safety culture. In this study, we implemented the TeamSTEPPS curriculum at two SNFs and obtained staff feedback and perceptions of the training. Methods: The TeamSTEPPS Fundamentals Course for Long-Term Care comprises 7 modules, each lasting 45-50 minutes. We adapted the training to address our setting's specific needs, focusing on creating the "Shift Change Checklist." After implementing training, SNF staff were surveyed on tool perception, the training program, safety culture, and feedback. Post-training focus group questions were derived from literature reviews. Answers were assessed for common themes by three independent reviews to identify categories. Results: Both facilities were able to successfully completed TeamSTEPPS training curriculum. 57 staff participated in training at Facility A, with 25 engaging in focus groups. At Facility B, 62 participiated, with six in focus groups. Facility A has beds of 122 while facility B has 46. Facility B reported successful shift change checklist implementation. Identified themes included communication, accountability, leadership, training, buy-in, and burnout. Discussion: Differences between the two facilities revealed factors influencing success or failure. Facility B's success may be attributed to consistently meeting basic staffing needs, a smaller patient population facilitating program implementation, and an assistant director of nurses driving the initiative. Despite Facility A's challenges, feedback indicated a staff community eager to enhance patient safety. The issues stemmed from external system factors rather than TeamSTEPPS curriculum limitations. Our data suggests TeamSTEPPS can be effectively implemented in an SNF, with external conditions influencing outcomes. Future studies involving diverse SNFs will clarify successful implementation factors. In summary, SNFs are integral in long-term care, and implementing TeamSTEPPS can enhance safety culture. Adapting the curriculum to specific needs, such as creating the "Shift Change Checklist," proved effective. Factors influencing success included staffing adequacy, patient population size, and leadership involvement. External conditions, not curriculum limitations, impacted implementation challenges. Despite difficulties, our findings support the promising implementation of TeamSTEPPS in SNFs, encouraging further research for targeted success in varied environments.
-

Impact of Vertical Zone Redesign: One Hospitals Experience
Zachary Shields, Enrique Alvarez-Ventura, and Curtis Johnson
Background: Crowding in the emergency department has been a prevalent issue for decades, however, over the last few years, crowding and the number of patient visits in EDs have been higher than normal. Many factors influenced this, including the COVID-19 pandemic. Emergency departments around the country have been at a loss in improving patient flow and time in the ER. Literature has demonstrated some possible methods with varying results, but there has not been significant research on the subject.
Methods: After reviewing the literature, we designed a system where patients were stratified between different groups using the triage system. If patients met any of the exclusion criteria as described, patients were placed in rooms. If the patients met the inclusion criteria, they were placed in the vertical zone, and the patient was then seen by a nurse and a provider. After placing orders, the patient was then moved to the waiting room. After this was done for 1 year the patient length of stay times (discharge/admission) were compared before and after the implementation of the vertical zone. Statistical analyses were performed calculating t and p values.
Results: The study included 33,949 patients with general demographics including age, sex, and group (vertical zone vs normal triage system) and evaluated multiple time factors for their stay. Patient volume remained the same compared to the previous year. The average low acuity length of stay was noted to decrease from 81.45 minutes to 71.64 minutes, a difference of 10 minutes (p=.05). The overall discharge length of stay was reduced from 158 minutes to 141 minutes (p=.04). There was no statistical difference between the average arrival to greet time, 6 minutes before the implementation and 5.5 minutes after the implementation. The average length of stay for admitted patients also significantly decreased from 315 minutes to 243 minutes (p=.0006).
Conclusion: In summary, by implementing this vertical zone redesign at our facility, low-acuity patient times were shortened by 10 minutes. The overall disposition time was shortened by 15 minutes to discharge over 11 months. This means that by continuing this practice in the future, patient's length of stay will decrease and patient flow will become more efficient overall. This study has provided tangible data on changing overall practice in respective hospitals now and in the future.
-

Implementation of Viz.ai Augmented Intelligence Software to Reduce Door to Puncture Times and Patient Outcomes at a Comprehensive Stroke Center
Cody Bryant, Brandon Womack, Mason Patel, and Sanjay Sharma
Introduction: Endovascular therapy (EVT) in the form of mechanical thrombectomy is the mainstay of treatment for acute large vessel occlusion (LVO) ischemic stroke, but its efficacy is highly time sensitive. It is crucial that stroke centers continue to implement process improvements that aim to streamline stroke workflow. Viz.AI is a platform that uses artificial intelligence to automatically detect LVOs with computed tomography (CT) imaging. It provides immediate access to the CT images as well as a platform for centralized communication through the mobile application. We sought to determine if the implementation of Viz.AI at our comprehensive stroke center improved stroke workflow and metrics. Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of all LVO stroke cases that underwent EVT at our facility from June 2020 through December 2022. Transfers and inpatient strokes were excluded. We compared periods before and after implementation of Viz.AI. The primary outcome was mean time of arrival in the emergency department to arrival at interventional radiology suite (EDIR). Rates of substantial reperfusion following EVT (modified thrombolysis in cerebral infarction score of 2C/3) were compared as a secondary outcome. Data was analyzed using t-test. Results: There were a total of 78 patients with LVO stroke who met inclusion criteria and underwent EVT from June 2020 to December 2022. There were 35 cases from June 2020 through June 2021 (pre-Viz.AI group) and 43 cases from July 2021 through December 2022 (post-Viz.AI group). Implementation of Viz.AI resulted in 16 min reduction in EDIR times (125 vs 109 minutes, P=0.09). There was no significant difference in rates of substantial reperfusion with EVT between groups (74% vs 71%). Conclusions: In patients with acute LVOs, there was no statistically significant improvement following implementation of Viz.AI at our facility.
-

Implementing a Standardized Screening Algorithm for Iron Deficiency Anemia in Pregnancy
Ariel Moskowitz, Nicole Tenzel, Joshua Mangels, and Lyndsay Millican
OBJECTIVE: Anemia in pregnancy is a global health problem and complicates >40% of pregnancies. Anemia is associated with significant maternal and fetal complications including low birth weight, preterm delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, ICU admissions, need for blood transfusion, and maternal morbidity. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the CDC recommend screening for anemia at the first prenatal visit and again between 24 and 28 weeks gestation. The aim of this quality improvement project is to improve compliance of screening for anemia in pregnancy amongst the providers of Medical City Women's Care. METHODS: Using the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement methodology, this project was developed to improve screening for anemia in pregnancy. We reviewed current recommendations from ACOG and the CDC to determine our screening protocol to include checking a CBC at each patients' initial prenatal visit, between 24-28 weeks gestation, and upon admission to the hospital for labor and delivery. We also implemented global screening for underlying hemoglobinopathies by performing a hemoglobin fractionation cascade at the initial prenatal visit. Providers and Medical Assistants at Medical City Women's Care were instructed on ordering CBC and hemoglobin fractionation at each patients' initial OB visit and an additional CBC between 24-28 weeks gestation. Laboratory order forms were updated with these recommendations and posted on all computer workstations. Comparison of pre-intervention and post-intervention compliance to the above screening protocol was performed. RESULTS: This study included 138 obstetrical patients from the Medical City Women's Care Clinic who established care prior to 20 weeks gestation between July 2023 and January 2024. We identified 3 patients with underlying hemoglobinopathies and 8 patients with baseline anemia at the initial prenatal visit. Compliance for screening for underlying hemoglobinopathy increased to 77%. Results for compliance of screening for anemia between 24-28 weeks gestation are pending, however we are anticipating a nearly 100% compliance rate based on preliminary data. CONCLUSION: Implementation of this project allowed us to improve screening for anemia in our obstetrical population at Medical City Women’s Care. This resulted in early detection of anemia which ultimately will lead to early treatment and improved admission hemoglobin at time of delivery. Prospective data from this study will be used to design a research project comparing admission hemoglobin pre- and post-QI implementation with the hopes of decreasing rates of blood transfusion in the immediate postpartum period.
-

Improving Clostridium Difficile detection at Medical City Arlington: A Quality Improvement Project
Bremmy Alsbrooks, Nur-Alhuda Shahub, Shabaz Mallick, Jesse Brown, Afsha Rais, and Afsha Rais
INTRODUCTION: Hospital acquired Clostridium difficile infection are one of the costliest hospital acquired infections. Over the past year, there were 19 C diff cases. Reasons for this uptick in cases from previous years could be waiting too long for collection (where a patient has C diff on admission, but does not receive testing until several days later), antibiotics, environmental (for example, using the same toilet brush to clean bathrooms on the floor as well as the bathroom in a C diff patient's room, cleaning high touch areas less than two times during the day, etc.), or staff education. From our meeting with the Infection Prevention team, there is a possibility that the recent cases in question were not hospital acquired, but resulted from failure to test a sample within the first three days or admission. Therefore, we sought to test this theory by researching staff understanding of the C diff MCA protocol. METHODS: A survey was created and distributed to various nursing staff, fellow residents, and physicians regarding the C diff protocol at MCA. The survey was distributed during scholarly activity presentations in resident didactics, lunch and learns, and during various other presentations throughout the hospital. Questions included when testing was appropriate, what can prevent C diff infections, if the participant had seen any C diff cases within the last year, and what was their understanding of the C diff protocol was. Questions were a mix of free response and yes or no. Approximately 196 responses were obtained from the survey. RESULTS: Although there was significant variability in the understanding of what contributed to the uptick in cases at MCA, roughly 50% of physician responses included a misunderstanding of the C diff protocol at MCA, specifically with regards to when testing should take place. These responses came from both attending physicians and residents. CONCLUSION: With these results, we conclude that one of the main issues affecting hospital acquired infections is staff education and when to test the sample. Therefore, we opted to create a infographic which would then be placed in high traffic areas, including the resident lounge and physician meeting room at the family medicine clinic. Through this infographic, we plan to better educate physicians about the MCA C diff testing criteria and to introduce our survey in one month to ensure that the information has been effectively relayed.
-

Improving Documentation of Patients' Physical Activity in the Outpatient Setting
Jordan Price, Syed Abbas, William Bass, Rigoberto Hernandez, Abdullah Shuaib, Michele L. McCarroll, and Lindsay Porter
Background: There is vast data on the health benefits of physical activity (PA) and the serious health consequences that are associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Research suggests that physicians who have meaningful conversations about exercise with their patients can be effective at increasing their patients' PA. In order to measure the effects of these discussions, the clinician must be able to document the baseline and subsequent PA of their patients. Our project seeks to improve the assessment and documentation of patient PA. Methods: Using Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement methodology, a multidisciplinary team was created to identify ways to improve documentation of patients' PA in the EMR. The team reviewed current policies and guidelines of PA documentation. Educational resources and training sessions were provided for clinic residents to appropriately ask and document PA. Comparison of pre-intervention and post-intervention adherence to charting recommendations was performed. Pre-intervention patients included a review of Medical City Grand Prairie Family Medicine patient records to identify PA documentation rates under the social history section of the patient encounter. Post-intervention patients beginning January 1, 2024 were identified in a similar manner, and documentation rates were analyzed at the 1, 2, and 3 month marks, respectively. Documentation and education reminders were regularly given to clinic staff before clinic began each day. Results: Appropriate documentation improved to x% in months 1,2, and 3, respectively, from a pre-intervention baseline rate of y%. Pre-interventionally, a% of patients were documented in social history as not exercising at all, b% of patients exercised moderately, and c% of patients exercised regularly. Post-intervention, these improved to d%, e%, and f% of no, moderate, and regular exercise, respectively. All documentation was reviewed by the residents performing the research. Conclusions: Promoting the questioning and documentation of a patient's PA can increase/decrease/have no effect on the EMR documentation rates at a primary care clinic. More promotion and education will be needed in the future to continue to identify patient populations with deficient amounts of physical activity, and assess responses to different exercise prescription (ExRx) interventions.
-

Improving Lesion Diameter Reporting on Skin Biopsy Requisition Forms: A Quality Improvement Project
Christopher Wong, Christian Scheufele, Marshall Hall, Henry Lim, Daniel A. Nguyen, Stephen Weis, Michael Carletti, and Dustin Wilkes
Background: Skin biopsy requisition forms (SBRFs) are the primary communication tool between dermatologists and dermatopathologists. Diameters of biopsied skin lesions are frequently omitted on SBRFs. This quality improvement project aimed to increase the rate of reporting diameters of neoplasms on SBRFs from an academic dermatology outpatient clinic to greater than 65% within three years. Methods: The Plan-Do-Study-Act model was utilized. An initial audit was performed for SBRFs of biopsies obtained between July 1, 2021, and February 4, 2022 (“Cycle 1”). On February 4, 2022, the authors discussed societal guidelines for lesion diameter reporting on SBRFs (“Intervention A”). Cycle 2 prospectively evaluated the efficacy of Intervention A by analyzing SBRFs from February 5, 2022, to June 14, 2022. Starting March 28, 2023, select SBRFs were physically stamped with visible reminders to include lesion diameter (“Intervention B”). Cycle 3 prospectively assessed the efficacy of Intervention B through SBRFs analyzed from March 28, 2023, to June 30, 2023. On July 1, 2023, a peer orientation, including Interventions A and B, was conducted for a new resident dermatologist (“Intervention C”). Cycle 4 prospectively evaluated the efficacy of Intervention C by analyzing SBRFs between July 1, 2023, to November 30, 2023. Results: Cycle 1 found 8.25% (49/594) of skin biopsies included lesion diameters on SBRFs. In Cycle 2, the reporting rate increased to 49.71% (85/171) in the intervention group, significantly higher than that of the control group (1.73%, 5/289). In Cycle 3, reporting rate increased in both the intervention (84.13%, 53/63) and control (26.80%, 78/291) groups. Cycle 4 saw further increases in the intervention (87.78%, 79/90) and control (37.62%, 155/412) group reporting rates. Conclusions: Each intervention increased lesion diameter reporting rate on SBRFs. Our interventions overcome common barriers to incorporating guidelines to improve quality (eg, inertia of previous practice, external barriers).
-

Improving Patients’ Perception of Provider Trust and Communication with Birth Plans
Christelle Reeves, Nicole Tenzel, and Timothy Kremer
Objective: Birth plans are an effective tool for a pregnant person to express their desires and expectations for labor and postpartum. Shortcomings of birth plans can be found whenever there is a lapse in communication between provider and patient. In the management of labor and emergent situations, it has been observed by patients that obstetric providers can communicate in authoritarian and dismissive manners. In response to this, birth plans were developed to serve as a guide in these scenarios. Birth plans allow a pregnant person to design a thoughtful plan of action with their healthcare provider before giving birth, rather than making critical decisions under stress. Our goal at Medical City Women’s Care clinic was to implement a standardized birth plan discussion between providers and pregnant persons. Standardized birth plan discussions would discuss analgesia in labor, emphasize breastfeeding benefits, and explain delayed cord clamping beginning at 32 weeks gestation. Methods: The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement cycle was utilized as a conceptual framework for this quality improvement project. An overview of the quality improvement project was presented to OBGYN resident physicians and attending physicians at Medical City Women’s Care. Project personnel presented birth plan importance and instructions on how to utilize birth plan questionnaire and documentation. Physicians were instructed to discuss the standardized birth plan by 32 weeks gestation and to document the responses in the clinic's EMR. Data was reviewed by month and analyzed by percent compliance. Compliance was noted if two of the three topics were discussed. Percent compliance was calculated by the number of documented birth plans divided by the total number of patients that were at least 32 weeks gestation during that month. Planned cesarean sections were excluded from data collection. Results: Within three months of project implementation, compliance was 80% for two consecutive months. Compliance then decreased to 50% for four consecutive months. Upon which, the location of documentation in the EMR was changed for ease and efficiency. Compliance then averaged to 75% for five consecutive months. Conclusions: Implementing a standardized birth plan discussion is possible using the PDSA methodology. The future goals of this project would be to ensure documentation of the birth plan in the labor admission note, and to explore how the standardized birth plan influences patient satisfaction in the birthing and postpartum experience.
-

Improving the Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm at Grand Prairie Internal Medicine Clinic
Riddhi H. Patel and Danielle Ford
Introduction: An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is typically defined as aortic enlargement with a diameter of 3.0 cm or larger. The prevalence of AAA has declined over the past 2 decades among screened men 65 years or older in various European countries. The current prevalence of AAA in the United States is unclear because of the low uptake of screening. This QI project will involve MCA residents and Grand Prairie clinic attending to incorporate screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm guidelines used by USPSTF and attempt to encourage all our established and new patients who fit into the criteria for screening to be screened for AAA. Methods: Baseline metrics for one-time screening for AAA in males aged 65-75 who are current or previous smokers were collected for the months of November 2022 to March 2024. This QI project will involve MCA residents and Grand Prairie clinic attending to incorporate screening via ultrasonography for abdominal aortic aneurysm guidelines used by USPSTF and attempt to encourage all our established and new patients who fit into the criteria for screening to be screened for AAA. Education will be given to all residents on why screening for AAA is important and complications that can arise from not undergoing screening. We developed a specific template on eClinicalWorks which will indicate the criteria of: current or previous smoker, age 65-75 years, and previously screened for AAA with ultrasound. There are posters in examination rooms. Resident training on missed one-time screening for AAA screening opportunities will occur over one-month time frame. Results: Before the beginning of this QI project, our Grand Prairie Clinic did not incorporate screening for AAA. From the months of November 22-April 2023 we saw a 10% increase. From May 2023 – October 2023 we saw 25% increase. November 2023 – December 2023 we have seen a 30% increase. Conclusion: Most AAAs are asymptomatic until they rupture. Although the risk for rupture varies greatly by aneurysm size, the associated risk for death with rupture is as high as 81%. This screening strategy at our clinic has contributed to this early diagnosis and prevention.
-

Increasing Online Reviews and New Patients in Clinic with QR Codes
Tristan Fun and Danielle Ford
Introduction: Patient census at the Medical City Internal Medicine Grand Prairie clinic has been lower comparatively to other HCA Healthcare clinics. Although the cause can be multifaceted, the clinic’s online presence (e.g. Google Maps) is minimal. One initial issue with the clinic’s online presence was the lack of reviews on the Google page for the clinic. One way to increase online reviews is to provide Quick Response (QR) codes in the clinic for patients to scan on their smartphone. The goal of this project is to increase the number of Google reviews for the clinic through QR codes to at least 1 per month. The number of new patients per month in the clinic will be tracked as a secondary outcome with a goal of a 10% increase in the number of new patients per month. Methods: QR codes were initially obtained from the Google website for the clinic and placed in the clinic. Data was collected manually by going through eClinicalWorks, the electronic medical record used in the clinic, to obtain the number of new patients. The monthly number of new patients in clinic and monthly number of online reviews posted was collected. Results: Prior to the start of the study, there was an average of 15.3 new patients per month (N = 3 months) and there was an average of 0.33 reviews per month. After starting the project with the first QR code placed, there was an average of 16.3 new patients per month (N = 4 months, p = 0.7726) and there was an average of 0.5 reviews per month (p = 0.8090). After the QR code was updated, there was an average of 22.2 new patients per month (N = 15 months, p = 0.2226) and there was an average of 0.53 reviews per month (p = 0.6684). Conclusion: At the end of the project timeline, the goal of the project was only partially met. While both the number of online reviews and number of new patients did increase, although not statistically significant, only the number of new patients met the goal of 10% increase while the number of online reviews per month was still below 1 per month. Future projects can focus on other factors that can increase patient census including improving online visibility on search engines and improving referrals to the clinic from the local community.





